Context:
I. The River Volga
II. Old Maina
III. New Maina
IV. Maina
V. Manych
I. The River Volga
In the middle course of the Volga River there are two rivers Maina and several settlements bearing this name. All of them have 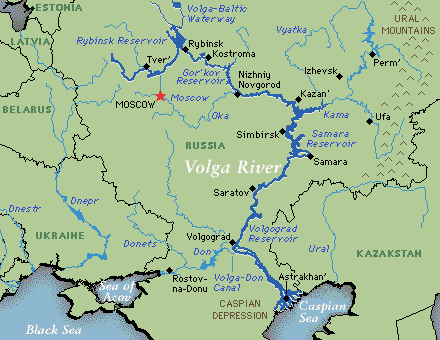 historical and sacral values described in the below sections of this work. They are largely based on the Volga, being a spiritual gift from Creator.
historical and sacral values described in the below sections of this work. They are largely based on the Volga, being a spiritual gift from Creator.
The Volga (3,692 km long) is one of the largest rivers on Earth and the largest in Europe. The Valdai in Tver region (Central Russia) is the origin of the Volga. Its mouth is the Caspian Sea. 11 of 20 largest cities of Russia, including its capital, Moscow, are located in the Volga’s watershed.
Along the Volga are located some of the largest reservoirs in the world. For example, Rybinsk Reservoir in the upper Volga. Interestingly, the city of Rybinsk is the birthplace of the founders of the Hollywood and the Russian residence of the Sweden born Nobels who made their fortune in Russia (including Baku oil), but best known for the Nobel Prizes.
The Volga is a great Russian river and has a special significance in Russian culture. It is often referred to as Mother Volga, the spiritual foundation of a multinational and multicultural Russian civilization, whose purpose is to be a spiritual beacon for the world.
Jose Arguelles has pointed out that ‘Rus’ (another name of Russia) is the ancient name of the force of harmonious ordering of phenomena. He is the man responsible for turning the eyes of the world to the Ancient Maya, and the profundity of Galactic Time Science and the father of the Harmonic Convergence of 1987 that was the key event for spiritual life of the planet and far beyond.
The magazine “World Channeling” No. 2 (27) 2016 provides interesting information about the common origin of the names of the Volga River and the country of Russia. It goes back to Lemuria. In those distant times the word ROUS meant CARRYING LIGHT, ENERGY CENTER, SPREADER OF ENERGY. Later, during the time of the Eurasian Hyperborea, the ROUS was the name of the river which is now known as the Volga. The city of Borea, the capital of Eurasian Hyperborea was also in the middle course of the Volga, on the territory of modern-day Kazan. This Eurasian Hyperborea was founded 8000 years ago the descendants of the Atlanteans who lived in the territory of modern Egypt. Kazan located on the Volga River is still Russia’s champion for the pyramids. The largest of them is a copy of the Great Pyramid in Giza.
Thus, the ancient Lemurian meaning of the word RUS and ROS is CARRYING ENERGY, ENERGY CENTER. The sound of OU during the time of Lemuria was not divided. Later, the sound OU was transformed either into a sound U, or into the sound O. In some words, these sounds alternate. That is why the words ROSSIYA (Russia) and RUS are simultaneously used. Lemurian language still exerts its influence on the Russian language.
Hence, the special task of Russians to learn how to feel harmoniously, develop the culture of their emotions and become the ROUS of LOVE or RUS of LOVE, the energy centers of love, which elevates all people to their Spiritual Motherland, the Motherland of Unconditional Love in the heart of the One God-Creator. There Love is one and inseparable. It is a special sacred center, the source of Love, the original energy of the highest sense. In English, the word HOME means a shelter, but even during the time of Lemuria it was known that HOUME is the heart of the God-Creator of the Universe. The connection with the Lemurian language is closely preserved in many languages of the world.
II. Old Maina
Old Maina (Russian: Staraya Maina) is an urban type settlement and the administrative center of the Old Maina district (Russian: 
Staromainsky raion) of Ulyanovsk region of Russia. It is located in the Volga Federal District. Its administrative center is the city of Ulyanovsk.
The Ulyanovsk region is the birthplace not only of Lenin (the symbol of Russian 1917 revolution that changed the world), but also of Russian writer, historian and critic Nikolay Karamzin (1766–1826), who is called the “father of Russian history” for his “History of the Russian State”, a 12-volume national history.
Old Maina claims to be the most ancient rural settlement in Russia. According to Ulyanovsk archaeologists, people on the territory of the present Old Maina have lived continuously for 1700 years. However, the oldest finds discovered on the territory of Old Maina are 20,000 years old. The territory of Old Maina and its surroundings are called archaeological Eldorado. As per the saturation of cultural heritage sites and their value, this area is unrivaled in the Ulyanovsk region, although the oldest part of Old Maina was flooded by the Kuybyshev Reservoir, sometimes called Samara Reservoir, created in the middle of the 20th century. It is the largest reservoir in Europe and third in the world by surface area.
The oldest artifacts found by archaeologists during the excavations in Old Maina, confirm the hypothesis of scientists that in the times of ancient Rus people began their movement from here (the Middle Volga) to the west to the rivers Don and Dnieper, mastering new territories, building new settlements, so was built the city of Kiev, now the capital of Ukraine. 1700 years ago Old Maina was a densely populated city with around 80,000 residents. Hense, Old Maina is much older than Kiev that is still considered one of the oldest cities in Russia, the mother of all Russian cities.
Historians and linguists know the lines from the oldest part of the Indian Vedas, the Rig-Veda, written in Vedic Sanskrit: “Itham ascati pasyat syantham, ekam starayath mainaa-kaalam” that is “There the holy rivers flow, the places are called Old Maina”. The Vedic phrase «starayath mainaa» is literally the Russian name of Old Maina — Staraya Maina…
Indeed, in the Rig-Veda are listed the names of dozens of holy rivers, on the banks of which the noble Vedic poets (Rishis) compose sacred hymns to the gods of the Rig-Veda. The Aranya Parva, also known as the “Book of the Forest” of Mahabharata (originally composed in Classical Sanskrit evolved from Vedic Sanskrit) has couple of hundreds names of the holy rivers (ponds) of Kurukshetra (the ancient Aryan land of Bharat) that cleanse a person from sins, after bathing in them. Interestingly, many of the Russian rivers of the Volga – Oka basin have preserved to this day their ancient names, given in the major holy ancient texts preserved in India.
The prominent researchers of ancient ties of Russia and India, point out that Russian language and Vedic Sanskrit are unusually close to each other, despite the millennia of their original way of development in Russia and India. The reason for this kinship is obvious. Both languages have one source of origin that is the Aryan language or Vedic Sanskrit of the Rig-Veda. Strong support for this also provides DNA-genealogy and huge number of Russian toponymy translated from Sanskrit. The Vedic names in the modern-day Sind province of Pakistan (the cradle of Vedic civilization of Hindustan) are similar to those in Russia. Most evident example is Karachi.
Vedic Sanskrit is not a dialect, but a complete and grammatically complex language. It is believed that all Indo-European languages have grown up from Vedic Sanskrit, including various and numerous dialects of the Slavic, Old Russian language. Sacred vocabulary is the basis of the Russian language. Indian sages well know that the Golden Age will begin in Russia.

Ancient Vishnu idol was found in Old Maina in 2007. Later that year, an international conference was organised to study the legacy of Old Maina. Surely, it might radically change the history of ancient Russia.
Based on the archeological findings, Old Maina can be recognized as the initial motherland of the Russian people and cradle of Russia. This brand will glorify Ulyanovsk region more than the status of the “homeland of Lenin”, who was born in Ulyanovsk in 1870.
The direct distance from Old Maina to Ulyanovsk is 45 km. By car it is less than 70 km. The road passes international Ulyanovsk Vostochny Airport that has the longest and the widest public use runway in the world. The airport is connected to the local state owned Aviastar plant, the largest aviation production facility in the world and one of the newest in Russia. Among the plant’s products  are: the An-124 long-range heavy transport aircraft, the 200-seat Tu-204 medium-range airliner, modernized Il-76, etc.
are: the An-124 long-range heavy transport aircraft, the 200-seat Tu-204 medium-range airliner, modernized Il-76, etc.
Until the Boeing 747-8F, the Antonov An-124 or RUSLAN was, for 30 years, the world’s heaviest gross weight production cargo airplane and second heaviest operating cargo aircraft, behind the one-off Antonov An-225 (a greatly enlarged design based on the An-124). The An-124 remains the largest military transport aircraft in the world.
The Ilyushin IL-76 has seen extensive service as a commercial freighter for ramp-delivered cargo, especially for outsized or heavy items unable to be otherwise carried. It has also been used as an emergency response transport for civilian evacuations as well as for humanitarian aid and disaster relief around the world. It is able to operate from unpaved runways and is used in many countries of the world.
The modernized IL-76 (IL-76MD-90A) now produced in Ulyanovsk has no analogues in the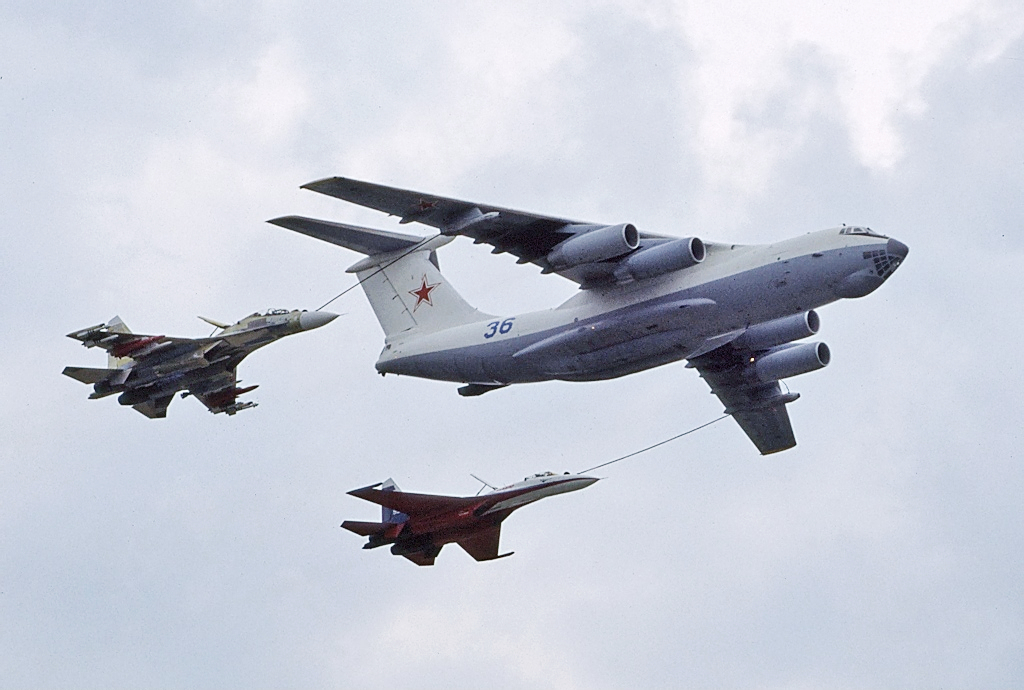 class of ramp vessels in the world. It can be operated in any climatic conditions with almost no restrictions. It could be used in various fields: as a military transport aircraft, aerial refueling tanker or command center, for extinguishing fires, etc. IL-76MD-90A is more unpretentious in comparison with the western one. It does not need a special infrastructure, and it does not need constant significant maintenance. They intend to create also a civilian version of the aircraft.
class of ramp vessels in the world. It can be operated in any climatic conditions with almost no restrictions. It could be used in various fields: as a military transport aircraft, aerial refueling tanker or command center, for extinguishing fires, etc. IL-76MD-90A is more unpretentious in comparison with the western one. It does not need a special infrastructure, and it does not need constant significant maintenance. They intend to create also a civilian version of the aircraft.
IL-76 and its modifications have been designed by the Ilyushin design bureau founded by Sergei Ilyushin (1894 – 1977) born near Vologda. He was the youngest of 11 children in a peasant family. Being largely self-taught, Ilyushin left home at an early age for Saint-Petersburg. He became an outstanding Soviet aircraft designer, the developer of the most massive combat aircraft in history (the IL-2 attack aircraft) rightfully considered the best attack aircraft of the Second World War. His IL-4 and IL-28 were the outstanding bombers. Being over 80 year old, Ilyushin Design Bureau has been leading not only in Russia, but also in the world. Ilyushin is the Russian presidential aircraft (board number one).
 In Old Maina there is a monument dedicated to the children who worked as hard as the adults during the World War II to crush the Nazis. On that monument it is written that Russia can not be defeated.
In Old Maina there is a monument dedicated to the children who worked as hard as the adults during the World War II to crush the Nazis. On that monument it is written that Russia can not be defeated.
By the order of Russian Tsar, fortress of Maina was founded in 1670 on the left bank of the Volga River, in  the mouth of local river Maina. According to Ulyanovsk archaeologists, in the territory of the present Old Maina people have been living continuously since the 3rd – 4th century. The tribes of Imenkovo archaeological culture came first here. Many official researchers regard Imenkovo culture as the Slavs. More profound results on the ancestors of the Slavs provide DNA Genealogy studies. They prove that the ancestors of the Slavs are the Aryans. It is also true for other nations living in the Russian Plain, Siberia, Central Asia, India, Iran, etc.
the mouth of local river Maina. According to Ulyanovsk archaeologists, in the territory of the present Old Maina people have been living continuously since the 3rd – 4th century. The tribes of Imenkovo archaeological culture came first here. Many official researchers regard Imenkovo culture as the Slavs. More profound results on the ancestors of the Slavs provide DNA Genealogy studies. They prove that the ancestors of the Slavs are the Aryans. It is also true for other nations living in the Russian Plain, Siberia, Central Asia, India, Iran, etc.
The ancient authors of the first centuries called the Volga as Ra. This is a very multilevel name. RA is the Sun of the Outer World, whereas AR is the Sun of the Inner World. Hence, the names Ariya and Aryan. In Sanskrit, Ra means fire. Ra is the ancient Egyptian god of the Sun. Ra is also one of the islands of Vanuatu (lit. “The land of happiness”).
Imenkovo culture was first discovered in village Imenkovo (Tatarstan), 100 km northeast of Old Maina, where river Kama meets the Volga. Both names are translated from Sanskrit. Imenkovo culture existed on the territory of the present Old Maina for about 400 years. The next five centuries the local lands were owned by the Volga Bolgars. Then these lands were conquered by the Golden Horde (Orda). After the collapse of the Golden Horde, the land was under the Kazan Khanate. In the second half of the 17th century the first Russian settlement from Moscovia appeared here.
Volga. Both names are translated from Sanskrit. Imenkovo culture existed on the territory of the present Old Maina for about 400 years. The next five centuries the local lands were owned by the Volga Bolgars. Then these lands were conquered by the Golden Horde (Orda). After the collapse of the Golden Horde, the land was under the Kazan Khanate. In the second half of the 17th century the first Russian settlement from Moscovia appeared here.
Unique archeological objects have been discovered on the territory of Old Maina. For instance, Gothic-type pendants dating from the 3rd century, coin of the Roman emperor Caracalla (dated the year of 213), etc. Each year more and more such rarities are found. On the territory of Old Maina they have found things connected with the Slavs, with the Balts, and even with the ancient Germans.
The remains of long houses, up to 25 meters in length, of German-type houses have been found on the land of Old Maina. Later, such houses appeared in the Vikings. The name of River Maina in Russia (tributary of the Volga) and the River Main in Germany (tributary of the Rhine) are genetically related. DNA genealogy shows that over 25% of modern male Germans have the same male ancestor with over a half of the Russian men. It is well known that large parts of Germany were populated by the Slavs. Their forceful 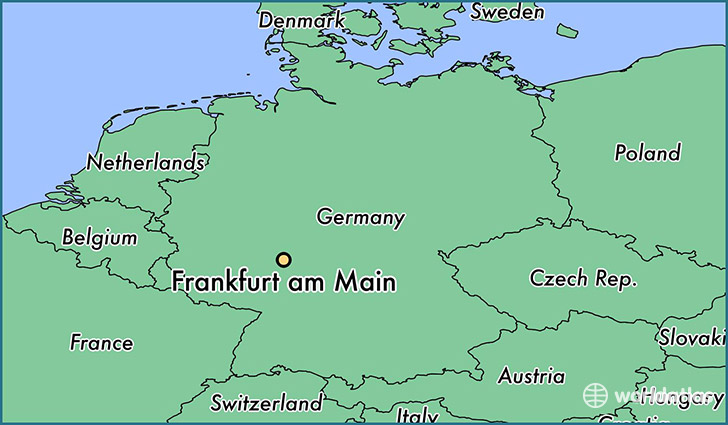 Germanization or extermination started approximately in the 12th century, when the Danish feudal lords destroyed the ancient Slavic sanctuary of Arkona, located on the island of Ruyan (German Rügen) in the Baltic Sea.
Germanization or extermination started approximately in the 12th century, when the Danish feudal lords destroyed the ancient Slavic sanctuary of Arkona, located on the island of Ruyan (German Rügen) in the Baltic Sea.

Frankfurt on the Main
The Main River (525 km) is also the longest river lying entirely in Germany. The largest city along the Main River is Frankfurt on the Main in the German state of Hesse, historically related to the Russian Imperial House of the Romanov and the founder of the most powerful family of Rothschild. Frankfurt is the major financial centre of the European continent. Messe Frankfurt is one of the world’s largest trade fairs. The Frankfurt Motor Show is the world’s largest motor show. The Frankfurt Book Fair is the world’s largest book fair. The River Main originates at the joining of its two headstreams, the Red Main and the White Main. The red and white are the colours of the flag of Frankfurt. They also symbolize the global mystery started in Ancient Egypt and centered today in the Russian town of Veliky Ustyug.


The wide mouth of River Maina near Old Maina is formed by the Volga’s water.
Archaeologically speaking, first settlers of the Middle Volga and Old Maina were the Imenkovo tribes, the first farmers in the Volga region. To date, scientists have identified more than 600 settlements and cemeteries of the Imenkovo culture. They were engaged in farming and cultivated millet, pound, wheat, barley, oats, peas, rye. A cattle breeding was very developed. The Imenkovo tribes bred horses, large and small cattle, and pigs. They had the processing of iron and bronze. Often are found iron plows, sickles, etc.
According to some sources, the Imenkovo tribes are considered to have come from the territory of modern Poland, Germany and Austria. Others believe that they came from the modern Ukraine. Exact answer on the ancestors of Imenkovo, and other tribes on the Russian Plain, the rest of Europe, and Siberia, provides DNA genealogy. Most importantly, the Ulyanovsk region is the only region that was completely the zone of settlement of the Imenkovo tribes. Neighboring regions were partly occupied by the Imenkovo culture. It was present only on their edges.
It has been substantiated that after the arrival of the Bolgarians in the Middle Volga region from the region of Azov Sea in 7th century, most of the Imenkovo culture bearers left to the southwest, where they became the nucleus of Volyntsevo culture (8th – 9th century) spread in the interfluve of the rivers Dnieper and Don. The village of Volynskoe (now part of Moscow) was the place of Stalin’s beloved residence. He died there in 1953.
In Kiev, layers of Volyntsevo culture are found in the most ancient places of the city, including the Church of the Tithes, the first  stone church in Kiev, built in the end of 10th century by the order of Grand Prince Vladimir the Great, who Christianized the Kievan Rus. Kiev was the main center of Christianization of other parts of Rus (Russia). Hence, it was called “mother of Russian cities” in Greek manner. The Greeks (from Byzantium) took the most active role in spreading Christianity in Russia. The expression “mother of Russian cities”, as well as the Greek “metropolis” (from “meter” – “mother” and “polis” – “city”), means the founding city. In Russian language, Kiev is a male name. Kiev reached its Golden Age as the center Kievan Rus in the 10th — 12th centuries.
stone church in Kiev, built in the end of 10th century by the order of Grand Prince Vladimir the Great, who Christianized the Kievan Rus. Kiev was the main center of Christianization of other parts of Rus (Russia). Hence, it was called “mother of Russian cities” in Greek manner. The Greeks (from Byzantium) took the most active role in spreading Christianity in Russia. The expression “mother of Russian cities”, as well as the Greek “metropolis” (from “meter” – “mother” and “polis” – “city”), means the founding city. In Russian language, Kiev is a male name. Kiev reached its Golden Age as the center Kievan Rus in the 10th — 12th centuries.
The non-legendary time of the founding of the Kiev is hard to ascertain. They say that Kiev is at least 1,200 years old. In Ulyanovsk region, Old Maina is 1,700 years old. However, the oldest Russian settlement is considered to be Tolbukhino (over 4,000 years old) near Yaroslavl, founded by Yaroslav the Wise (circa 978 – 1054), thrice grand prince of Veliky Novgorod and Kiev, uniting the two principalities for a time under his rule. His descendants were 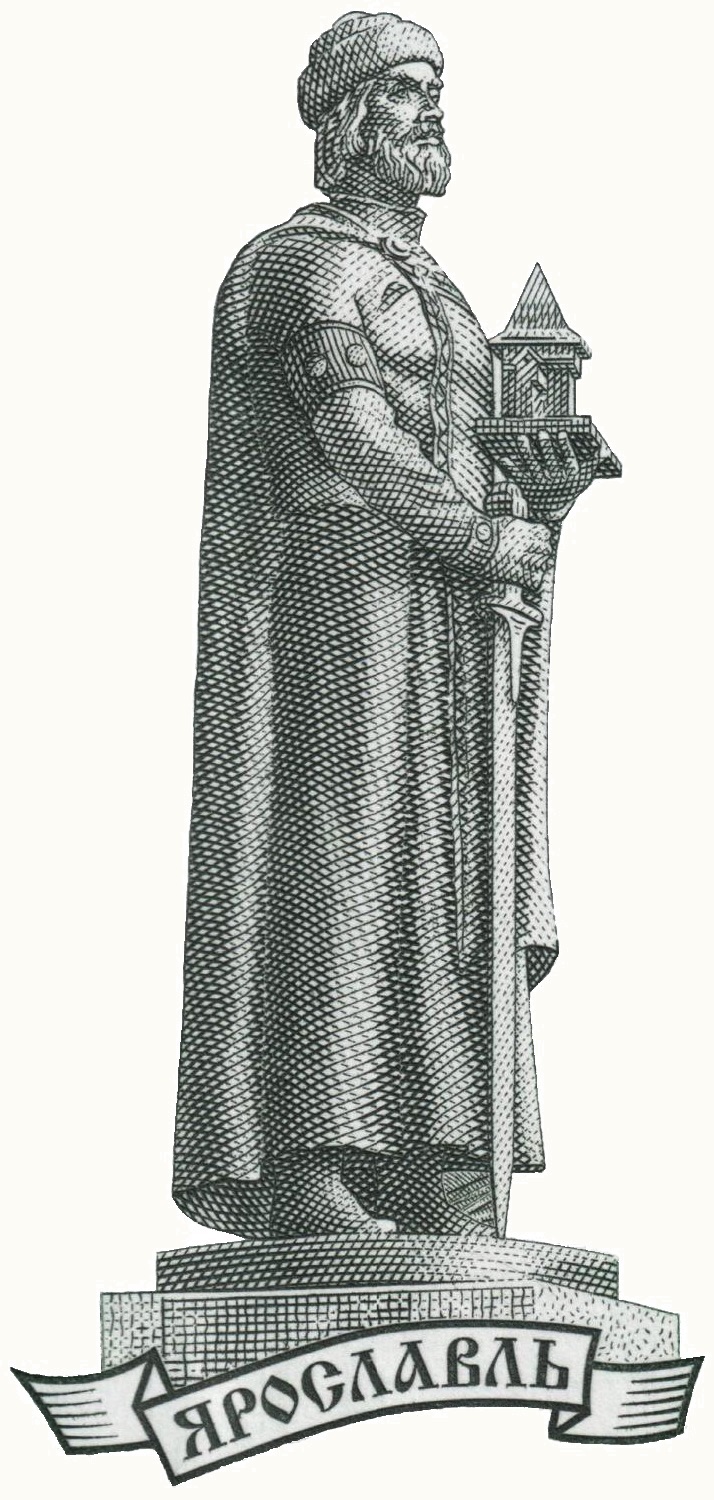 deeply involved in The Knight Templar in France and Palestine. The oldest settlement on the territory of modern-day Yaroslavl belongs to the 5th – 3rd millennium BCE. Apparently, Kazan and Yaroslavl are the oldest of all the currently existing cities on the River Volga. The name Yaroslavl sounds related to Yaruslim, the capital of Lemuria.
deeply involved in The Knight Templar in France and Palestine. The oldest settlement on the territory of modern-day Yaroslavl belongs to the 5th – 3rd millennium BCE. Apparently, Kazan and Yaroslavl are the oldest of all the currently existing cities on the River Volga. The name Yaroslavl sounds related to Yaruslim, the capital of Lemuria.
Magazine “World Channeling” states that in the sky over Yaroslavl, in subtle plans, there is the Yaroslavl Temple. This is one of the most important places and points of the planet, existing in many worlds and dimensions. Portals of a huge number of galaxies and civilizations flock here.
Yaroslavl is a multi-level temple. It is possible to decipher the name of the city of Yaroslavl as “the glorification of the Spring Sun”: YAR means “the Sun”; SLAVL means “to praise”. However, here there is a shortened version of the name of the Sun. The hidden meaning is YARUN (YARILO), which in meaning is the Central Spiritual  Sun, and not the Sun of the Solar System itself. Yaroslavl is the point of the Earth, which has always been directly connected with the energy flows of the Central Spiritual Sun. The bear is the ancient symbol of Yaroslavl, like Russia’s. According to a legend, when Yaroslav the Wise came here to baptize the local residents, he had to
Sun, and not the Sun of the Solar System itself. Yaroslavl is the point of the Earth, which has always been directly connected with the energy flows of the Central Spiritual Sun. The bear is the ancient symbol of Yaroslavl, like Russia’s. According to a legend, when Yaroslav the Wise came here to baptize the local residents, he had to  deal with their sacred and worshiped bear. It happened at the confluence of the Volga and the Kotorosl River.
deal with their sacred and worshiped bear. It happened at the confluence of the Volga and the Kotorosl River.
While many bearers of the Imenkovo culture went from the territory of present-day Tatarstan to the territory of modern Ukraine, some of them remained in place and merged with the incoming nomads Bolgarians, and influenced their culture and economy, in particular the development of agriculture. The Bolgarians were migrating from the region of Azov Sea after the dissolving their Great Bolgaria (Great Bulgaria), existed in mid-7th century between the River Dniester and lower Volga, (modern southern Ukraine and south-west Russia). The original capital was Phanagoria on the Taman peninsula between the Black and Azov seas. The first major part of Bolgar tribes (Orda) led by khan Asparukh moved to the north-eastern Balkans, to the River Danube. In 681, these Bolgars formed with the local South Slavic tribes the First Bulgarian Empire. The second major part of Bolgar tribes moved to the Middle Volga and formed the Volga Bolgaria. From these medieval times, Bulgaria on the Danube River is the direct relative with Bolgaria (Bulgaria) on the Volga River. There is a hypothesis that the original name Bolgar is connected with Russian / Slavic name Volgar that means a person from the Volga River.
Still not everyone in the scientific world agrees with the Slavic ethnic attribution of the Imenkovo culture, and often this is based not so much on scientific caution, but on political reasons. The largest scientists believe that the Imenkovo culture was formed by the bearers of the ethnonym Rus. These Russians leaved precisely from the lands where these Imenkovo tribes lived, and formed a new Volyntsevo culture that formed the above mentioned Kiev (modern capital of Ukraine and former capital of Kievan Rus, a loose federation of East Slavic tribes existed from the late 9th to the mid-13th century. The question “Where did the Russian land come from?” receives a precise answer. Most scientists know this, it was the Middle Volga. The Imenkovo culture began the development of the Volyntsevo culture of the Middle Dnieper. The Imenkovo culture is Rus. Hence, the land of present-day Old Maina and the basin of River Maina can be considered the very territory from which the Russian land (state) came from.
The source of the river Maina is located over 50 km west from Old Maina, on the territory of Tatarstan (often associated with Tartarus), close to the border with the Ulyanovsk region. Actually, the River Small Maina (tributary of river Maina) is the line of border between the Republic of Tatarstan and the Ulyanovsk region. The source of the river Maina is in the Spassky District of Tatarstan. The main attraction of this district and its  administrative center is the town of Bolgar, located on the left bank of the Volga River, like Old Maina. The distance between Bolgar and Old Maina is 40 km.
administrative center is the town of Bolgar, located on the left bank of the Volga River, like Old Maina. The distance between Bolgar and Old Maina is 40 km.
Bolgar was the medieval capital of Volga Bulgaria from the 8th to the 15th centuries. It was a big international trade center, linking the East and the West by the Volga trade route. Traders from China, Baghdad, Damascus, Spain, Scandinavia, Rus and other countries used to come to Bolgar. Many foreign trade concessions had their settlements and streets in Bolgar. It is stated that Bolgar was bigger than Paris and London. Bolgar is a World Heritage Site declared by the UNESCO World Heritage Committee.
 Bolgal has special religious significance for the Muslims of Russia and the Volga river regions in particular. Islam was adopted here in 922 and it became official religion of the Volga Bulgaria. Special embassy arrived from Baghdad then capital of the Caliphate ruled by the Abbasid dynasty. The spread of Islam in the Middle Volga region was peaceful. The Volga Bulgarians knew One God from their pre-Islamic religion called Tengrism. The adoption of Islam by the Volga Bulgaria led to a strong impetus to the development of education, literature, and science. The Bolgars achieved considerable success in mathematics and astronomy, chemistry and medicine, geography and history. From the Soviet times, pilgrimage to Bolgar is called the Little Hajj.
Bolgal has special religious significance for the Muslims of Russia and the Volga river regions in particular. Islam was adopted here in 922 and it became official religion of the Volga Bulgaria. Special embassy arrived from Baghdad then capital of the Caliphate ruled by the Abbasid dynasty. The spread of Islam in the Middle Volga region was peaceful. The Volga Bulgarians knew One God from their pre-Islamic religion called Tengrism. The adoption of Islam by the Volga Bulgaria led to a strong impetus to the development of education, literature, and science. The Bolgars achieved considerable success in mathematics and astronomy, chemistry and medicine, geography and history. From the Soviet times, pilgrimage to Bolgar is called the Little Hajj.
Today, Islam is the religion of about 1,5 billion inhabitants of the Earth. It  is more than 22% of the world’s population. The largest Koran is kept in Bolgar. The Volga Bulgaria was the only Islamic country of Eastern Europe. The Bulgarian Historical and Architectural Museum-Reserve (established in 1969) is the most northern monument in the world of medieval Muslim architecture. Being secular, the leadership of Tatarstan places a key importance on the development of historical and religious heritage. Bolgar is identified with Islam, whereas Sviyazhsk is recognized as the first Christian center in Tatarstan.
is more than 22% of the world’s population. The largest Koran is kept in Bolgar. The Volga Bulgaria was the only Islamic country of Eastern Europe. The Bulgarian Historical and Architectural Museum-Reserve (established in 1969) is the most northern monument in the world of medieval Muslim architecture. Being secular, the leadership of Tatarstan places a key importance on the development of historical and religious heritage. Bolgar is identified with Islam, whereas Sviyazhsk is recognized as the first Christian center in Tatarstan.
Sviyazhsk is located at the confluence of the Volga and Sviyaga Rivers. The source of the River Sviyaga (375 km) is located in the Ulyanovsk region, on the right side of the Volga, 60 km south from the urban settlement Maina.
III. New Maina
New Maina (Russian: Novaya Maina) is an urban type settlement of the Ulyanovsk region. New Maina is located 70 km southeast of Old Maina, and 90 km southeast of Ulyanovsk. Only 9 km is to New Maina from the city of Dimitrovgrad.
southeast of Old Maina, and 90 km southeast of Ulyanovsk. Only 9 km is to New Maina from the city of Dimitrovgrad.
 New Maina and Dimitrovgrad are divided by the river called the Big Cheremshan (Russian: the Bolshoy Cheremshan River), a tributary of the Volga River.
New Maina and Dimitrovgrad are divided by the river called the Big Cheremshan (Russian: the Bolshoy Cheremshan River), a tributary of the Volga River.
Cheremshanka is the name of a number of settlements in Siberia, including Krasnoyarsk Cheremshanka Airport, located 25 km north of the mouth of river Mana. Between them there are two creeks named Big Arey and Small Arey. They are tributaries of the Kacha River (tributary of the Yenisei River). Arey and Arya refer to the Aryans lived here thousands years ago. In Sanskrit, “kaccha” means “watery soil”, “a bank or any ground bordering on water”, “shore”, “a mound or causeway”, etc. Beside the Kacha River in Krasnoyarsk in Southern Siberia, Russia has settlement and river Kacha in Crimea, where it enters the Black Sea near Sevastopol.
Being the second-largest city of the Ulyanovsk region (“the motherland of Lenin”), Dimitrovgrad was named in 1972 celebrating the posthumous 90th birthday of Georgi Dimitrov, the first communist leader of People’s Republic of Bulgaria. It is also symbolic taken into account that the Volga Bolgars (Bulgars) and the Bulgarians divided in 7th century to establish first Bulgarian state on the Danube and another on the Volga. Dimitrov ruled Bulgaria from 1946 to 1949. He led the Moscow based Communist International from 1934 to 1943. He expanded Lenin’s ideas by stating that fascism was the dictatorship of the most reactionary elements of financial capitalism.
Russian Dimitrovgrad is twinned with Bulgarian Dimitrovgrad. Also, Dimitrovgrad of the Ulyanovsk region is twinned with city of  Obnisk (the Kaluga region), the place of the world’s first nuclear power plant to generate electricity for a power grid.
Obnisk (the Kaluga region), the place of the world’s first nuclear power plant to generate electricity for a power grid.
Founded in 1714, modern Dimitrovgrad is a prominent nuclear center of Russia. The city’s leading enterprise is the country’s Federal Nuclear Research Institute. One of the institute’s atomic reactors provides Dimitrovgrad with district heating.
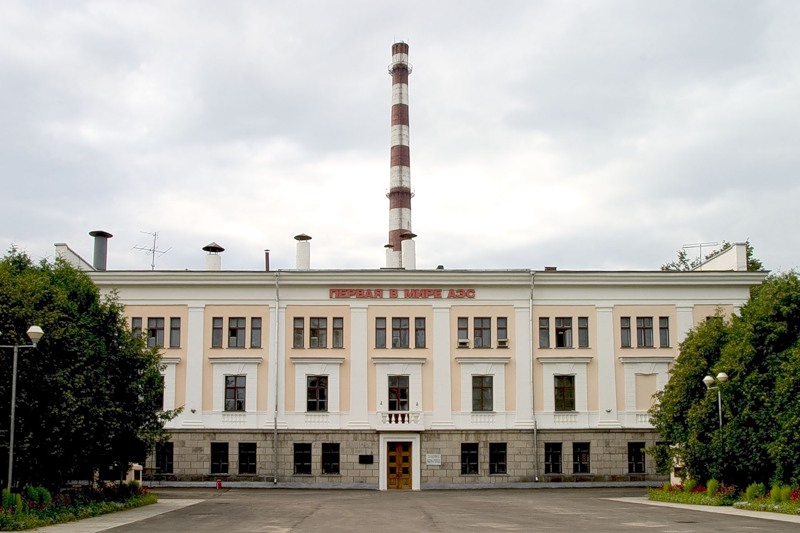

Obninsk. The world’s first nuclear power plant
Unlike the US military who dropped in 1945 two nuclear bombs on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki (located near the 33rd parallel), Russia (then the Soviet Union) pioneered peaceful use of atomic energy. Russia built the first nuclear power plant on the planet that started in 1954 producing electricity for Moscow region. It was the first nuclear power plant in the world connected to national power grid. This reactor in Obninsk (the Kaluga region) was stopped in 2002. Today the station is a memorial museum of the nuclear industry in Russia. This world’s first home of a peaceful atom is open to visitors and tourists.
Symbolically, Kaluga is the place of Russian rocket scientist Konstantin Tsiolkovsky (1857 – 1935) who is the founding father of modern rocketry and astronautics. His works inspired leading Soviet rocket engineers, including Sergei Korolev the father of practical astronautics, who was in charge of the development of the R-7 Rocket and launching into Cosmos the first man (Yuri Gagarin) and later the first woman (Valentina Tereshkova, born near the above mentioned Yaroslavl).
Dimitrovgrad also has the State Scientific Center of Russian Federation, Research Institute of Atomic Reactors. The farther of Russian nuclear program and the peaceful atom Igor Kurchatov (1903 – 1960) was born in the Urals, the natural border between the East and the West, and the most sacral place on the planet.
Dimitrovgrad / New Maina are located 110 km north of Samara. It has given its name to the Samara culture, a neolithic culture of  the 5th millennium BCE. The Samara region is considered as the original homeland of the Proto-Indo-European language.
the 5th millennium BCE. The Samara region is considered as the original homeland of the Proto-Indo-European language.
Samara is one of the largest cities in the Volga River, and the 6th largest city in Russia. Samara is a major international transport hub. Its railway station is the tallest in Europe.
Samara’s most prominent symbol is the Monument of Glory, overlooking the Volga river. It is a man with wings raised over his head, standing on the pedestal symbolizing ray of light rising to the sky. The city is well known in the world for the production of aerospace launch vehicles, satellites, various space services, engines, aircrafts, etc. Samara has been one of the largest Russian aircraft manufacturing centers. It is the home of the Samara Research Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences and Samara State Aerospace University, one of Russia’s leading engineering and technical institutions.
During the Great Patriotic War / Second World War (1941 -1945) Samara was the reserve (second) capital of the Soviet Union. Highly  secretive bunker of its ruler Josef Stalin is now open to the public. After the war, Samara became the Cosmic capital of the Soviet Union. In Samara was built the launch vehicle Vostok, which delivered in 1961 the first manned spaceship to orbit with Yury Gagarin on board. After returning to Earth / landing near the great Russian River Volga,
secretive bunker of its ruler Josef Stalin is now open to the public. After the war, Samara became the Cosmic capital of the Soviet Union. In Samara was built the launch vehicle Vostok, which delivered in 1961 the first manned spaceship to orbit with Yury Gagarin on board. After returning to Earth / landing near the great Russian River Volga,  Yury Gagarin, the first man to travel in Space, took a rest in Samara. Here he reported to the State Commission, headed by Sergei Korolev, on the successful completion of his historical mission.
Yury Gagarin, the first man to travel in Space, took a rest in Samara. Here he reported to the State Commission, headed by Sergei Korolev, on the successful completion of his historical mission.
It became a tradition for the Soviet astronauts to come to Samara after returning to Earth. Beside implementation of the space program, Samara enterprises have been playing a leading role in the development of aviation. One of its symbols is the above mentioned Ilyushin Il-2 ground-attack aircraft assembled in Samara in late 1942. During the World War II, Samara produced During produced over 15,000 of Il-2 of more than 36,000 built in the Soviet Union. So, the Il-2 remains to this day the most massive and effective combat aircraft in history. After the War, for more than half a century Samara produced Tupolev, Antonov and Ilyushin-designed aircrafts. The vast majority of Tupolev Tu-154 airplanes (over a thousand aircrafts), which formed the basis of the Soviet Union and Russia’s civil aviation from the 1970s to the early 2000s, were manufactured in Samara. A veritable icon of the Cold War, four-engine turboprop-powered strategic bomber and missile platform, Tupolev Tu-95 was also produced in Samara.
Near Samara in 1391 there was a great battle between the Samarkand ruler Tamerlan and Tokhtamysh, a descendant of Genghis Khan and a prominent khan of the Golden Horde (Orda). This confrontation had a huge impact on the history of Eurasia.
Tamerlan (“The One Who Knows Merlin”) had the symbol of Shambala as his personal seal. According to the Roerichs, who worked with the Mahatmas of Shambala, Tamerlan owned the Cintamani Stone received from the Shambala. This Stone was originally a gift from Orion and considered responsible for spiritual evolution on Earth. Chintamani strengthens the power of the owner, contributing to victory in any endeavor. Cintamani was in the hands of Solomon, Alexander the Great, Genghis Khan, Tamerlan, Akbar the Great, Napoleon, the Roerichs. The country where the Stone arrives, receives the special protection of the Brotherhood of Light.
It is stated that due to such protection, Tamerlan never lost a single battle. Tokhtamysh was indeed his strong opponent. These two armies were the strongest in Europe and Asia at that time. Even after two severe defeats from Tamerlan, Tokhtamysh was able to pull together his Golden Horde to resist and attack again.
The Horde’s military power peaked during the reign of Uzbek (1312–1341), who adopted Islam and ruled from capital Sarai-Batu in the lower part of the Volga River, 100 km north from modern city of Astrakhan, where the Volga River begins to enter the Caspian Sea. The territory of the Golden Horde at its peak included most of Eastern Europe from the Urals to the Danube River. It extended east deep into Siberia. The Golden Horde’s lands incorporated the Black Sea, the Caucasus Mountains, and bordered the territories of present-day Iran and Azerbaijan, ruled by the Mongol dynasty known as the Ilkhanate. Iran (literally “the country of Aryans”) and Northern Azerbaijan are related to the Manna Kingdom existed there in the 1st millennium BCE.
New Maina is located in the lower parts (close the mouth) of three rivers: the Big Avral, the Small Avral, and the Dry Avral. In Sanskrit, Avirala means “compact”, “contiguous”, “dense”, etc. New Maina was founded in the second half of the 18th century. Before the 1917 Revolution, New Maina was a district containing a number of villages. Its status of urban type settlement New Maina got in 1973. Symbolically, 73 is the car code of Ulyanovsk region (for number plates).
IV. Maina
 The above described settlements Old Maina and New Maina of the Ulyanovsk region are located on the left bank of the River Volga. On the opposite right bank of the Volga, there is also settlement Maina and river Maina. This urban type settlement Maina is 50 km west south of Ulyanovsk, whose historical center is also on the right bank of the Volga. Interestingly, in Southern Siberia also there is settlement called Maina.
The above described settlements Old Maina and New Maina of the Ulyanovsk region are located on the left bank of the River Volga. On the opposite right bank of the Volga, there is also settlement Maina and river Maina. This urban type settlement Maina is 50 km west south of Ulyanovsk, whose historical center is also on the right bank of the Volga. Interestingly, in Southern Siberia also there is settlement called Maina.
Maina is administrative center of the Maina district of Ulyanovsk region. In the vicinity of the settlement are the sources of the rivers Maina and Berezovka. Interestingly, beside the link to the Russian name of the Birch (Bereza), the term Berezovka (Bereza) could be also connected to the Hara Berezaiti (literally meaning “High Watchpost”) given in the Avestan language to a legendary mountain around which the stars and planets revolve. Indeed, the Ulyanovsk region is a part of the Volga Uplands (Volga Hills) that are also famous for their unreal beauty.
The Avestan language is the language of Zoroastrian scripture of the Avesta. There is a hypothesis that Zoroaster was born near modern Russian city of Perm, the Urals region. Perm is located on the Kama River (Sanskrit name), 630 km north east of Ulyanovsk. The River Kama meets the Volga River 110 km north east of Ulyanovsk. The mouth of Volga is the Caspian Sea linking modern Russia and Iran.

 The Avestan language is classified as an Iranian language, a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages within the Indo-European family. The Avestan is assumed to have been quite close to Vedic Sanskrit. In Russia there are many names of rivers and settlements translated from Sanskrit. For instance, in the Ulyanovsk region is the source of river Sura. In Sanskrit, Sura means “water, sage, sun, divinity’”.
The Avestan language is classified as an Iranian language, a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages within the Indo-European family. The Avestan is assumed to have been quite close to Vedic Sanskrit. In Russia there are many names of rivers and settlements translated from Sanskrit. For instance, in the Ulyanovsk region is the source of river Sura. In Sanskrit, Sura means “water, sage, sun, divinity’”.
160 km west of the source of the River Sura is the source of another Sanskrit name River Moksha, literally meaning “Nirvana”. The source of the Sura River is 90 km west south of the settlement Maina and the sources of rivers Maina and Berezovka.
The River Maina is the Volga’s drainage basin: the Maina (23 km long) → the Barysh (247 km long) → the Sura (841 km long) → the Volga (3,692 km long) → the Caspian Sea.
 70 km northwest from Maina is the settlement
70 km northwest from Maina is the settlement  Sura Peaks (Russian: Surskiye Vershiny). This place is famous for its St. Nicholas Hill overlooking the River Sura. It is one of the most revered destinations in the Sura district and the whole Russia. It is believed by everyone claimed the 76-meter hill will be freed from all the sins. This St. Nicholas Hill is made of chalk. Its slopes are very steep, covered with grass and rare bushes.
Sura Peaks (Russian: Surskiye Vershiny). This place is famous for its St. Nicholas Hill overlooking the River Sura. It is one of the most revered destinations in the Sura district and the whole Russia. It is believed by everyone claimed the 76-meter hill will be freed from all the sins. This St. Nicholas Hill is made of chalk. Its slopes are very steep, covered with grass and rare bushes.
40 km north of St. Nicholas Hill / the settlement Sura Hills is located city of Alatyr, founded in 1552 near the conjunction of the River Alatyr and the Sura River.  Alatyr, like the settlement Sura Hills, was established by the order of the first Russian Tsar Ivan Grozny going to conquer Kazan.
Alatyr, like the settlement Sura Hills, was established by the order of the first Russian Tsar Ivan Grozny going to conquer Kazan.
Anagrams of Alatyr (or vice versa) are: Altair (the brightest star  in the Aquila constellation), Altar (the ‘Holy table’, structure for religious sacrifices located in places of worship), etc. Altai Mountain is the most sacred place in Russia. In the Russian medieval legends and folklore, Alatyr-stone is a sacred stone, “the father to all stones”, and the navel of the Earth, containing sacral writings. The Alatyr-stone is endowed with healing and magical properties. In the spiritual verses it is stated that from beneath the Alatyr-stone originates a wonderful source that gives the whole world sustenance and healing.
in the Aquila constellation), Altar (the ‘Holy table’, structure for religious sacrifices located in places of worship), etc. Altai Mountain is the most sacred place in Russia. In the Russian medieval legends and folklore, Alatyr-stone is a sacred stone, “the father to all stones”, and the navel of the Earth, containing sacral writings. The Alatyr-stone is endowed with healing and magical properties. In the spiritual verses it is stated that from beneath the Alatyr-stone originates a wonderful source that gives the whole world sustenance and healing.
 The source of river Alatyr is 190 km west of its mouth. The Alatyr originates in the Nizhny Novgorod region, near town of Sarov, most known for its St. Seraphim of Sarov and the Russian center for nuclear research. Sarov is a sister city to Los Alamos, the home of the U.S. nuclear weapons design laboratory. The scientists of Sarov (former Arzamas-16) and Los Alamos have cooperated on various arms control and nuclear safeguards programs. The Russians playfully called their own center «Los Arzamas».
The source of river Alatyr is 190 km west of its mouth. The Alatyr originates in the Nizhny Novgorod region, near town of Sarov, most known for its St. Seraphim of Sarov and the Russian center for nuclear research. Sarov is a sister city to Los Alamos, the home of the U.S. nuclear weapons design laboratory. The scientists of Sarov (former Arzamas-16) and Los Alamos have cooperated on various arms control and nuclear safeguards programs. The Russians playfully called their own center «Los Arzamas».
 Between St. Nicholas Hill / the settlement Sura Hills and city of Alatyr is located village Sara and two Sarka rivers: The Big Sarka and the Small Sarka. Sarka is a diminutive of Sara (river). In Sanskrit, Sara means “essence”, “stream”, “energy”, “main point”, etc. The Middle Eastern name Sarah means “Princess”.
Between St. Nicholas Hill / the settlement Sura Hills and city of Alatyr is located village Sara and two Sarka rivers: The Big Sarka and the Small Sarka. Sarka is a diminutive of Sara (river). In Sanskrit, Sara means “essence”, “stream”, “energy”, “main point”, etc. The Middle Eastern name Sarah means “Princess”.
The Sara River is also in the center of Moscow, although now it is enclosed in a tube. This Sara is a tributary of the Moscow River. In Yaroslavl region of Russia, 180 km northeast of Moscow, the Sara River enters the Lake Nero, whose name is related (or vice versa) with the surname of Jawaharlal Nehru, the first Prime Minister of independent India. His daughter Indira Gandhi and grandson Rajiv Gandhi were also Prime Ministers of India and central figures in Indian politics.
 100 km south of Maina, 45 km southwest of the source of the Sura River is the settlement of Kanadei that is quite close to the name Canada and the surname Kennedy, or vice-versa. The most famous romance of John F. Kennedy was with Hollywood actress Marilyn Monroe. She was made a star by the founder of Hollywood, a former Russian subject Joseph Schenck, born in Rybinsk, located in the Upper Volga. Talent of Monroe was developed by her Russian teachers who found themselves in America.
100 km south of Maina, 45 km southwest of the source of the Sura River is the settlement of Kanadei that is quite close to the name Canada and the surname Kennedy, or vice-versa. The most famous romance of John F. Kennedy was with Hollywood actress Marilyn Monroe. She was made a star by the founder of Hollywood, a former Russian subject Joseph Schenck, born in Rybinsk, located in the Upper Volga. Talent of Monroe was developed by her Russian teachers who found themselves in America.
Kanadei is located in the conjunction of the River Kanadeika with the Syzranka River. A tributary of the River Kanadeika is Ardovat. Also, Ardatov is a Russian town located 20 west km of Alatyr.
40 km north from Kanadei is the source of Sviyaga River, a tributary of the Volga River. In the city of Ulyanovsk, the Sviyaga River (375 km long) flows only a few kilometers away from the Volga River (3,692 km long), but their confluence is 160 km north of Ulyanovsk, in Tatarstan. Tsar Ivan Grozny built in the 16th century in the mouth of Sviyaga River a fortress Sviyazhsk.
200 km west of Kanadei is the source of Sanskrit named river Moksha, literally meaning Nirvana. The River Moksha is a tributary of the River Oka, the Volga’s drainage basin.
The River Kanadeika is also the Volga’s drainage basin: Kanadeika (57 km long) → the Syzranka River (168 km long) → the Volga (3,692 km long) → the Caspian Sea.
Kannada is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly by Kannada people in India, mainly in the state of Karnataka, having deep ties with Russia, including the state symbols, the Roerichs, Helena Blavatsky, еtc. It is believed that the name Karnataka, translated from the local Kannada language, means “an elevated country”. It is also the true for the Russian settlement Kanadei and the River Kanadeika, located in the Volga Hills (the Volga Uplands). The source of the River Kanadeika is only 22 kilometers south of the settlement Sura Peaks (Russian: Surskiye Vershiny), where the Sura River originates.
The son of the god Surya, Karna is one of the central heroes of the Mahabharata. He is the embodiment of strength, valor and honor. In Sanskrit, “karna” means “eared”. In Russian there is surname Karnaukhov having same meaning. In Kemerovo region, a man with surname Karnaukhov is said to have discovered the famous Tisulsky Princess.
The Ulyanovsk region has many Sanskrit names crucial to Indian culture, founded by the Aryans came from the territory of modern-day Russia. If read from right to the left in Arabic, Rusia (Russia) becomes Suria. It is not only the Arab-speaking country of Syria, but also the above described Vedic god Surya and Russian River Sura.
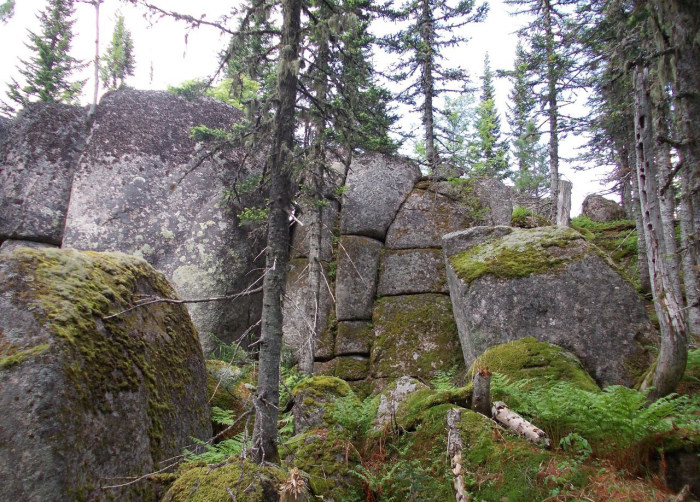
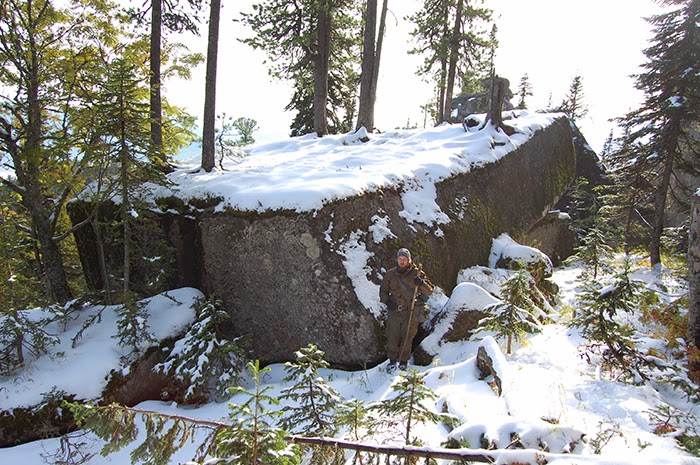
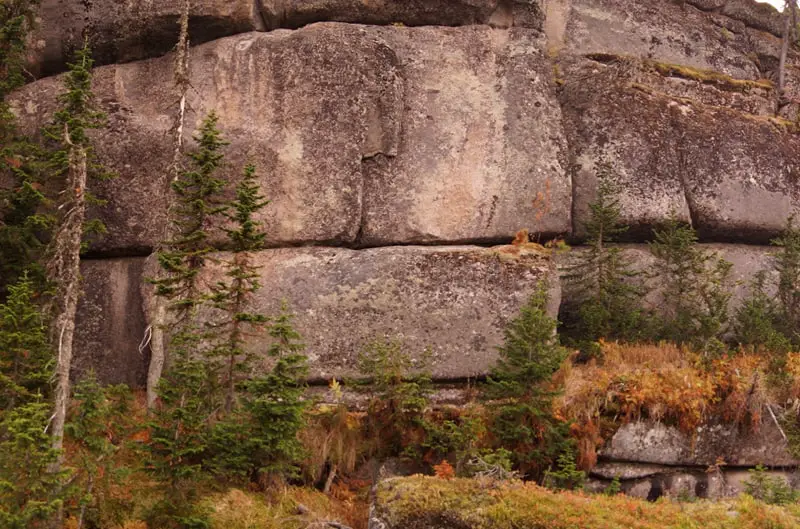
100 km south from Ulyanovsk or 90 km southeast of Maina is mysterious equilateral triangle (roughly with sides 15 km * 15 km *15 km) in the hills covered by beautiful pine forest, widely known for unusual gardens of huge bizarre-shaped stones, curving of space and time, strong natural energy coming from the Earth around the so called Devil’s finger, underground passageways, sudden appearance of UFO and aliens, etc.
Near this triangle, was born Ivan Dmitriev (1760 – 1837), a famous Russian statesman, member of the Russian Academy, and poet. By the personal invitation of Emperor Alexander I, he served as Minister of justice from 1810 to 1814. Ivan Dmitriev underlined the intrigues, following first of all the law. Due to his honesty he got into many conflicts with influential dignitaries. However, Alexander I highly respected him. Also, Ivan Dmitriev was a distant relative of Nikolay Karamzin (1766–1826), the “father of Russian history”.
V. Manych
In Southwestern Russia there are two rivers with the root “Man”: the East Manych (basin of the Caspian Sea) and the Western Manych (basin of the Azov Sea).
The East Manych (141 km long) and the Western Manych (420 km long) both originate in the Republic of Kalmykia, located in the southwestern part of European Russia. A small part of the Volga River flows through eastern Kalmykia. Also, Kalmykia is washed by the Caspian Sea in the southeast.
The distance between the sources of both Manych Rivers and the Caspian Sea is about 250 km. There are many legends about the Manych River. According to old scriptures it flowed from the Caspian Sea. There is an assumption that in ancient times the Manych River was a large strait that united the modern Caspian Sea and the Black Sea.
The salinity of the lakes in the basin of the River Manych indicates the existence of a connection with the sea basins. Presumably, the strait ceased to exist 3,000 years ago. However, for a long time the ancient tribes used Manych as a navigable artery connecting the Azov Sea coast (the Don delta region) with the Caucasus. By the Manych, goods were transported from China, Persia, Turkestan and India, merchants sailed from the Caspian. The Phoenicians (known for their marine and trading skills) sailed to the Caspian Sea along the Manych strait. In the middle of the 19th century, fragments of an ancient sea vessel of supposedly Phoenician origin, made of cedar wood with copper nails, were washed in the shore of Manych.
Interestingly, Kalmykia is the only region in Europe where Buddhism is the most practiced religion. The majority of the Kalmyks follow Buddhism, like their ancestors, the westernmost group of the Mongols whose ancestral home is in the Altai region of western Mongolia. They migrated from the steppes of Southern Siberia to the Lower Volga region in 17th century and became subjects of the Russian Tsar. They duty was protecting Russia’s southern border.
The Western Manych, often called just Manych (420 km long) is tributary of Don (1,870 km long), one of the major rivers of Russia and the 5th longest river in Europe. The Volga and the Don are the two main waterways of the European part of Russia. They approach each other in the modern-day Volgograd region. The importance of connecting the Volga and the Don by means of a canal was clear as early as the Middle Ages. The earliest attempt to link them, dates back to 1569, when the Turkish sultan Selim II sent 22,000 soldiers to dig a canal between the two rivers. The Turks gave up after a month of work. Selim II or Sarı Selim (“Selim the Blond”) was a son of Suleiman the Magnificent and Hurrem Sultan, often called Roxelana, one of the most powerful and influential women in Ottoman history. Hurrem means “the cheerful one” in Persian, but she was Russian, from the territory of modern-day Ukraine. By large, the Russians, the Persians, and the Turks have the Aryans as their ancestors.
Another attempt to connect the Volga and the Don was made by the Russian Emperor Peter the Great (1672 – 1725), who defeated the Turks in Azov (mouth of the Don) in 1696. The canal was partially completed by the end of 1701, but the Russo-Swedish war broke out, and the Emperor had to abandon the project.
Only the Soviet Union was able to realize the old dream of linking the two great rivers  that connect five seas: the Baltic, White, Caspian, Azov and Black seas. Shipping Volga – Don Canal named after Lenin was opened in 1952 in Southwestern Russia. The canal’s length is 101 km. It connects the Volga River and the Don River at their closest points. The canal starts south of modern Volgograd (Fortress of the Volga), where the lower course of the Don approaches the lower course of the Volga.
that connect five seas: the Baltic, White, Caspian, Azov and Black seas. Shipping Volga – Don Canal named after Lenin was opened in 1952 in Southwestern Russia. The canal’s length is 101 km. It connects the Volga River and the Don River at their closest points. The canal starts south of modern Volgograd (Fortress of the Volga), where the lower course of the Don approaches the lower course of the Volga.
Volgograd (former Stalingrad) is a hero-city. It is famous for its heroic resistance to the Nazis and the bitter defeat of the Naz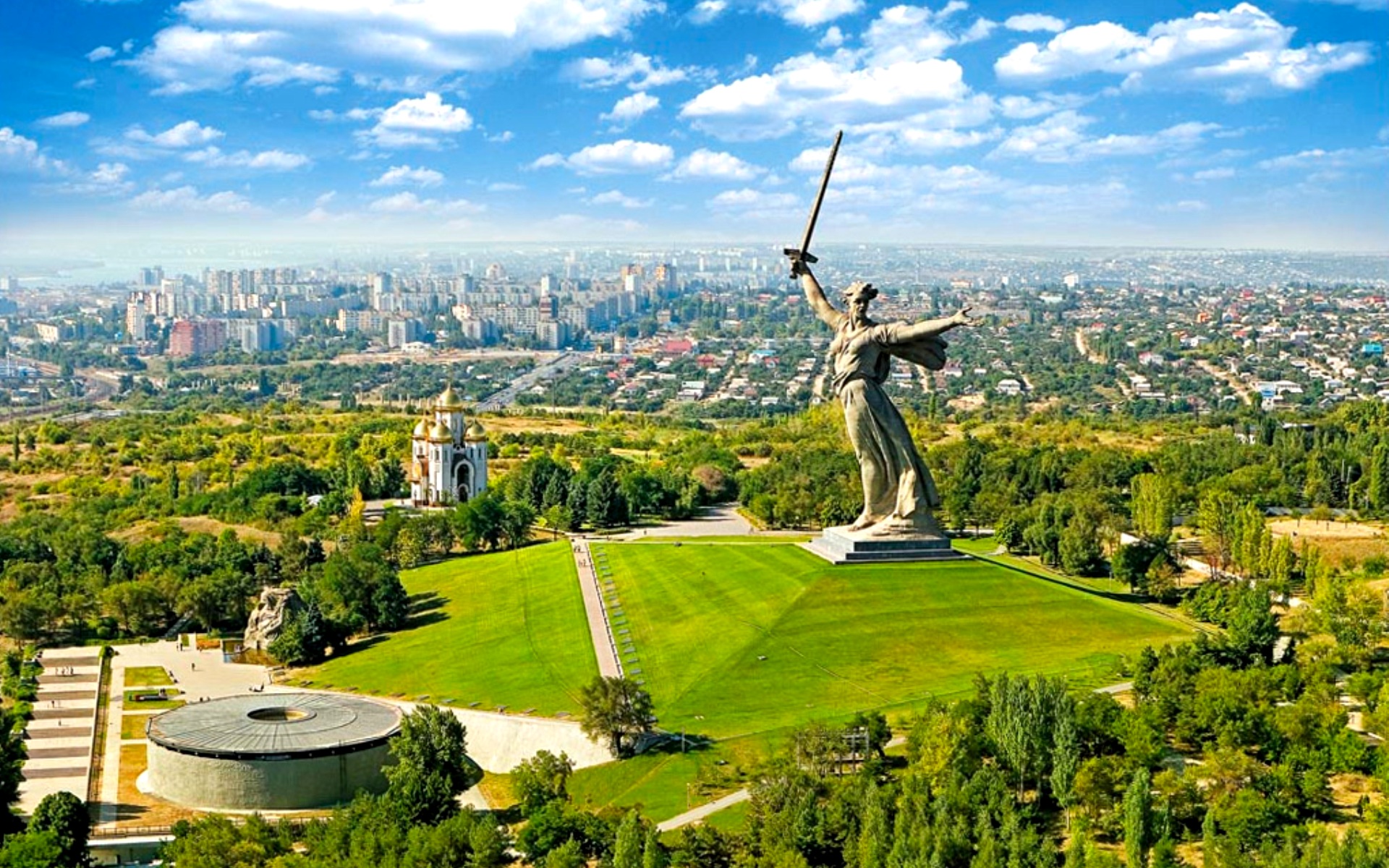 is from the Soviet defenders during the Battle of Stalingrad (August 1942 – February 1943) that was the largest and bloodiest battle in the history of warfare.
is from the Soviet defenders during the Battle of Stalingrad (August 1942 – February 1943) that was the largest and bloodiest battle in the history of warfare.
In the mouth of the Manych is the settlement Manych (Russian: Stanitsa Manychskaya) named after the river. Initially, it was a fortress founded by the Don Cossacks in 16th century to fight against the Ottoman Turks occupied their land. At that time the Don Cossacks enrolled on the service to the Russian Tsar Ivan Grozny and the whole Muscovy or Rus.
Interestingly, the name of Osman I (1299 – 1324), the founder of the Ottoman Empire, might be related to Atman or Ataman. It is the original title of Cossacks’ leader. According to Ottoman tradition, Osman’s father led his tribe west from Central Asia into Anatolia, fleeing the Mongol onslaught. Central Asia is the home land of the descendants of the Aryans. Although they speak different languages now and live in different countries, genetically they share the common ancestor.
The settlement Manych is located 40 km east of the city of Rostov-on-Don, a major international transport center, a port of five seas: the Black Sea, the Sea of Azov, the Caspian Sea, the White Sea, and the Baltic Sea. Rostov-on-Don is and the administrative center of the Southern Federal District of Russia and also often referred as the “gateway to the Caucasus”. The main city Cathedral of Virgin’s Nativity was designed by Konstantin Ton (1794 – 1881), an official architect of Imperial Russia during the reign of Nicholas I. His most prominent works include: the Cathedral of Christ the Saviour (with mysterious Elohim on the main dome), the Grand Kremlin Palace and the Kremlin Armoury in Moscow.
Rostov-on-Don and nearby city of Tagangor are the places of the Southern Federal University (founded in 1915). It is a large scientific and educational center of Russia. In 2016, the university entered the rating of the best universities in the BRICS countries.
Besides being a large educational center, Rostov-on-Don is a worldwide center for helicopter and farm machinery manufacturing.
Rostvertol (founded in 1939) is a leading Russian helicopter manufacturer company located in Rostov-on-Don. It has been
producing helicopters designed by the Mil design bureau since 1956 and is a world leader in the manufacture of heavy-lift helicopters. The plant also produces unique combat attack helicopters, operated in many countries.
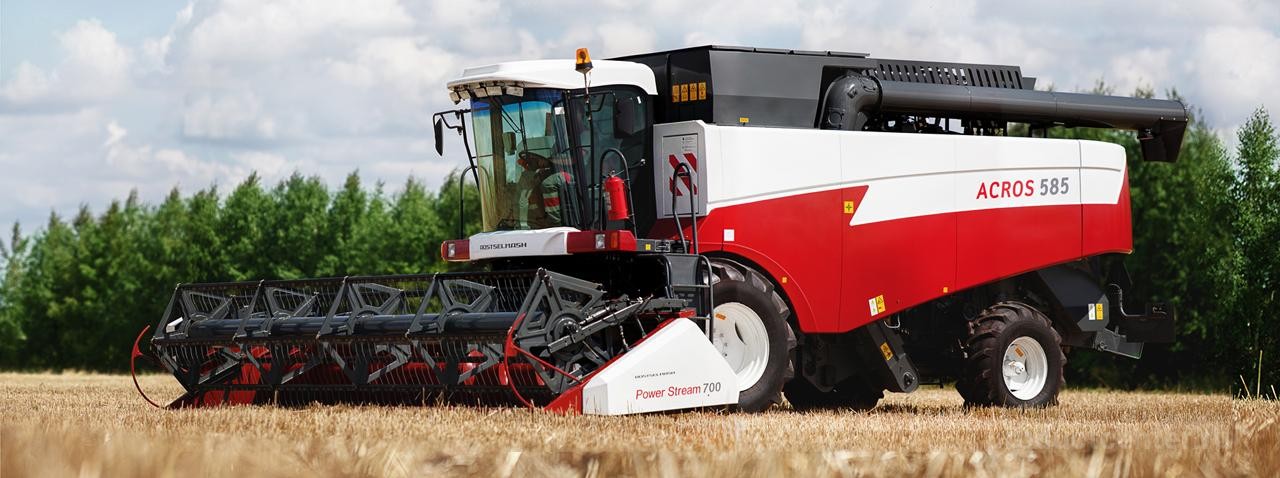 Rostselmash (founded in 1929) is a Russian agricultural equipment company, based in Rostov-on-Don. It is one of the five largest world producers of agricultural machinery. Beside Russia, Rostselmash has production facilities in Canada, USA, Ukraine and Kazakhstan.
Rostselmash (founded in 1929) is a Russian agricultural equipment company, based in Rostov-on-Don. It is one of the five largest world producers of agricultural machinery. Beside Russia, Rostselmash has production facilities in Canada, USA, Ukraine and Kazakhstan.
Novocherkassk Electric Locomotive Plant (founded in 1936) is the largest Russian manufacturer of electric locomotives and  one of the largest manufacturers of locomotives in the world. The plant has produced more than 16,000 locomotives of more than 65 types. Its locomotives haul trains transporting 80% of all cargo on the electrified railways of Russia and CIS countries. Russia has the longest railway in the world. The longest railway in Russia and on the planet is the Transsiberian Railway (9,300 km long), also called The Great Siberian Way, connecting Moscow with the Far Eastern industrial cities of Russia. Russia has a total length of 121,000 km of the railway tracks, most being located in picturesque areas.
one of the largest manufacturers of locomotives in the world. The plant has produced more than 16,000 locomotives of more than 65 types. Its locomotives haul trains transporting 80% of all cargo on the electrified railways of Russia and CIS countries. Russia has the longest railway in the world. The longest railway in Russia and on the planet is the Transsiberian Railway (9,300 km long), also called The Great Siberian Way, connecting Moscow with the Far Eastern industrial cities of Russia. Russia has a total length of 121,000 km of the railway tracks, most being located in picturesque areas.
Beriev Taganrog Aviation Scientific Technical Complex (founded in 1934) is the world leader, specializing in amphibious aircrafts.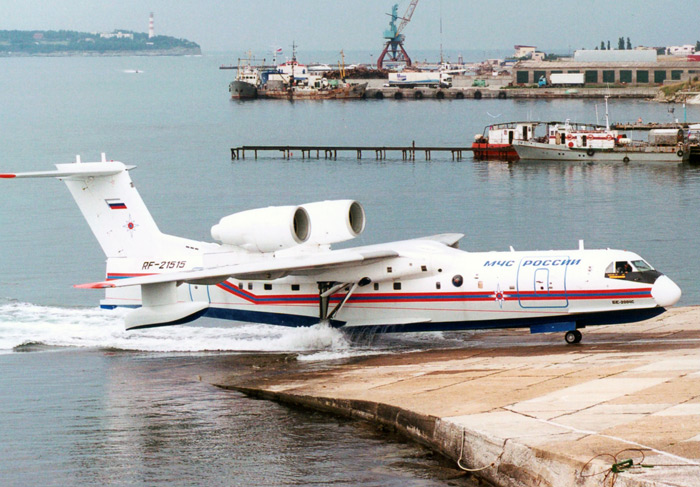  Throughout its history, it has designed and produced more than 20 different models of aircraft for civilian and military purposes, as well as customized models. Pilots flying Beriev seaplanes have broken 228 world aviation records.
Throughout its history, it has designed and produced more than 20 different models of aircraft for civilian and military purposes, as well as customized models. Pilots flying Beriev seaplanes have broken 228 world aviation records.
Then Beriev Design Bureau was moved to Krasnoyarsk in Southern Siberia in 1942 to avoid destruction in World War II, and returned to Taganrog in 1945. Near Krasnoyarsk is the mouth of river Mana.
A pioneer of amphibious aircraft was an Italian-born Soviet aircraft designer and scientist Robert Bartini (1897 – 1974), alumni of Polytechnic University of Milan. He lived and worked in Taganrog (50 km of Rostov-on-Don). “Every 10-15 years the cells of the human body are completely renewed, and since I lived in Russia for more than 40 years, I did not have a single Italian molecule left”, wrote Bartini. He influenced many Soviet aircraft engineers, particularly the future “father of Soviet Space program” Sergei Korolev who named Bartini as his teacher. Bartini was connected with other prominent Soviet aircraft engineers such as Ilyushin, Antonov, Myasishchev, Yakovlev and many others. Bartini was one of the most famous engineers in the Soviet Union, nicknamed Red Baron because of his noble descent. On the account of Robert Bartini are over 60 successful aircraft projects in the Soviet Union. Without Bartini, there would be no Sputnik, the first artificial Earth satellite, launched by the Soviet Union in 1957.
In 1974, three months priory his death, Bartini made a report, in which he proposed aircraft carriers on hydrofoils. This aircraft carrier would be moving at the speed of 600-700 km/h, so that the aircraft could land without quenching speed. When Bartini made his report, shipbuilder Rostislav Alexeyev of Sormovo (Nizhny Novgorod), a prominent designer of hydrofoil ships and developer of ground effect vehicles, refused to make his report, citing the fact that his report was worse.
Taganrog is located in Taganrog Bay, the northeastern arm of the Sea of Azov. The direct distance between Taganrog and the mouth of River Don is 25 km. Often Taganrog Bay is perceived as a flooded estuary of the Don River. Rostov-on-Don is the main city on the river.
 In antiquity, the Don was viewed as the border between Europe and Asia by some ancient Greek geographers. Indeed, the modern boundary of Europe and Asia is drawn by the Manych, a tributary of the Don. The border passes along the tops of the Ural Mountains and further along the Kumo-Manych depression, which is now the floodplain of the Kuma and Manych rivers, but in ancient times was a strait connecting the Black Sea with the Caspian.
In antiquity, the Don was viewed as the border between Europe and Asia by some ancient Greek geographers. Indeed, the modern boundary of Europe and Asia is drawn by the Manych, a tributary of the Don. The border passes along the tops of the Ural Mountains and further along the Kumo-Manych depression, which is now the floodplain of the Kuma and Manych rivers, but in ancient times was a strait connecting the Black Sea with the Caspian.
There are two segments of the Asian-European border, which cause the bitterest disputes. This is a site to the south of the Ural Mountains (to the Caspian Sea) and a jumper between the Caspian and Black Seas. In the first case, the problem is caused by the fact that in the southern part of the Urals the ridge falls into several spurs. Still it is not accurately determined, which of them is to consider the border of Europe and Asia. As for the border section in the Caucasus region, there are also several opinions. Some scientists propose to draw a border along the Kumo-Manych lowland, others — along the watershed of the Caucasian Range, the third — to the south. It is obvious that the establishment of the border between Europe and Asia is not only a scientific, but also an administrative, and a political dilemma. By large, Asia is the home to the world’s first modern civilization, over 60% of total world population, and the largest economy of all continents.
Russia has parts in Europe and Asia. It is like balancing the Matter and the Spirit (ancient mystery), left and right hemispheres of human brain, male and female, etc. In order to solve the issue of Europe-Asia border, Russian scientists proposed to use not only geographical, but also political, and cultural-civilizational approach. The Asia Council (a forum for Asia’s heads of state or government and key decision makers) provides the most interesting facts about Asia.
According to Plutarch, the Don River (i.e. Europe-Asia border) was also home to the legendary Amazons of Greek mythology. During the times of the Scythians, near Rostov-on-Don (in the mouth of the Don) there was an ancient town and a major trading route known in Greek as the Tanais. This place (the Don River delta) Norwegian explorer Thor Heyerdahl has identified as the place of Asgard, the adore of Odin and his gods.
During the times of the Scythians, near Rostov-on-Don (in the mouth of the Don) there was an ancient town and a major trading route known in Greek as the Tanais. This place (the Don River delta) Norwegian explorer Thor Heyerdahl has identified as the place of Asgard, the adore of Odin and his gods.
Internationally, Colchis is perhaps best known for its role in Greek mythology. It was the destination of the Argonauts, the home to Medea and the Golden Fleece. In more ancient legends, there is evidence that the legendary Argonauts, and later the ancient Greek  hero Hercules, searched for Colchis in the delta of River Don (the Azov Sea). Aea, later Colchis, was located in the lands of the Azov (not the Black) Sea. The name of Colchis was fixed by famous Ancient Greek lyric poet Pindar.
hero Hercules, searched for Colchis in the delta of River Don (the Azov Sea). Aea, later Colchis, was located in the lands of the Azov (not the Black) Sea. The name of Colchis was fixed by famous Ancient Greek lyric poet Pindar.
According to commonly spread tales, the Argonauts made their famous voyage to the shores of Colchis, located somewhere in the mouth of the Rioni River, flowing through the territory of modern Western Georgia (the Caucasus) washed by the Black Sea. However, this interpretation is not the oldest, and there are other texts. In the archaic, the most ancient versions of myths of the Argonauts, rooted in the 13th century BCE, the place of their action is the Don (Tanais), but not Rioni.
The authors, who composed their historical works in the Archaic time (at least 500 years before Hellenism), located Colchis in the delta of the Don River. In 13th century BCE, the real Colchis and its capital were located in the delta of the Don. In the 3rd century BCE, the memories of Aea / Colchis were transferred to Georgia. In the oldest myths, the Argonauts sought the Golden Fleece on the banks of the Don. Only in Hellenistic times, Greek and Roman poets began to localize Colchis in Georgia.

Kobyakovo hillfort
If the capital of Colchis had been on the territory of the Georgian Colchis, then archaeological evidences would have been in the place. However, so far archaeological science doesn’t know any cities of the Bronze Age in the Georgian Colchis, which could be identified with the legendary capital of the Colchis. On the other hand, in the delta of Don River such settlements are in abundance. One of the most famous is Kobyakovo hillfort, associated with the capital of the Colchis according to some ancient descriptions and archeological findings. Unique is the Kobyakovo archaeological culture of the Bronze Age, discovered on the eastern border of modern city of Rostov-on-Don. This city’s name has something in common with the name Frankfurt-on-Main. Interestingly, the distance to settlement Manych (the mouth of River Manych) from Rostov-on-Don / Kobyakovo hillfort is only 30 km.
Moreover, Kobyakovo hillfort has an exclusive layer of a relatively high civilization of the Copper Age, linked with the Aegean world of the Mediterranean Sea located between the Greek and Anatolian peninsulas, i.e. between the mainlands of modern-day Greece and Turkey. Copper, as provide by numerous extracted objects, was melted on the spot. The Copper Age existed before the Bronze Age. The Copper Age began in the late 5th millennium BCE.
The oldest securely dated evidence of copper making is 7,500 years ago. It has been discovered in an archaeological site in Serbia (motherland of Constantine the Great). The archaeological site of Belovode on the Rudnik Mountain in Serbia contains the world’s oldest securely dated evidence of copper smelting at high temperature from 5,000 BCE. Interestingly, the word “Rundik” (English: mine) is exactly the same in the Serbian and the Russian languages. Serbian Belovode fully correlates to the Russian term Belovode meaning Shambala. It is associated with Altai Mounties. In the past, Altai was among the major metal producing regions of Russia. The first capital of the Serbs was Ras (now a World Heritage Site) in Raska, a Serb medieval state, being centered in the region of Raška (hence its exonym). Serbs call southwestern Serbia, Kosovo and its former parts as Raska or Old Serbia.
Back in the 19th century, historians and archaeologists noted the fact that there was nothing like Kobyakovo archaeological culture in Russia or abroad. It is a phenomenon in the history of mankind, largely refuting the rights of Sumerians and Egyptians on creation of the first terrestrial civilizations. Moreover, the Sumerians and Egyptians stated that all their knowledge and essential technologies, including metalwork, were given to them by gods, i.e. representatives of highly developed civilizations.
Rostov-on-Don was named after the church of St. Dmitri of Rostov (1651 – 1709), located in the fort on the bank of River Don. St.  Dmitri was a prominent Russian Church theologian, Bishop of Rostov that is a town in present-day Yaroslavl region. The origin (etymology) of the word “Rostov” is uncertain. In the spoken Russian Rostov is pronounced as Rastov. In the ancient Egyptian Ra was sun god.
Dmitri was a prominent Russian Church theologian, Bishop of Rostov that is a town in present-day Yaroslavl region. The origin (etymology) of the word “Rostov” is uncertain. In the spoken Russian Rostov is pronounced as Rastov. In the ancient Egyptian Ra was sun god.
In pre- dynastic Egypt, Rushaa or Rasha (compare to Russia) meant Head or Headland. Located on the Nile meridian, the Giza Plateau was known as Rastau or Rostau. Giza was the place of the god Osiris, who was the Lord of the underground tunnels existing under the Giza Plateau. Being the early names for the Giza Plateau, Rastau also represented the shafts of the Pyramids that lead to the stars and mouth of the passages. Spiritually, Rastau or Rostau (quite close to Rostov or vice versa) symbolized portals between worlds. Chief Egyptian god Osiris was called Lord of Rastau. Interestingly, the residents of Russian Rostov were the founders of modern-day town of Veliky Ustyug where Egyptian Osiris has turned to Ded Moroz.
After all, the Kobyakovo hillfort located in Rostov-on-Don is not only one of the most mysterious points on the archaeological map of Russia, but also an anomalous zone. There are many legends, folk beliefs, and facts that cannot be explained.
For the first time the phrase “Kobyakovo hillfort” is found in a letter of July 7, 1570, by Ambassador Ivan Novoseltsev to Tsar Ivan Grozny. People lived on Kobyakov hillfort for millennia without a break. Only from 6th to 1st centuries BCE, there was a break for several centuries. It has been suggested that the year 23 of our era is the earliest date fixed by a reliable epigraphic monument of first mentioning the inhabitants of “ancient Rostov”. It is considered the starting point of the two thousand-year official history of Rostov-on-Don. Such a historical concept, although controversial, deserves attention.
In modern culture and literature, the Don region is also famous due to the epic novel “And Quiet Flows the Don” written by Mikhail Sholokhov (1905 – 1984), winner of the 1965 Nobel Prize in Literature. Sholokhov lived and worked in a rural locality (stanitsa) Vyoshenskaya, located in on the Don River, in the northern reaches of the Rostov-on-Don region. Today Vyoshenskaya is regarded as the spiritual heart of the Don region.
While the lower Don was well known to ancient geographers, its middle and upper parts were not mapped with any accuracy. The source of River Don was associated with the country of Scythes. The River Don originates in the modern city of Novomoskovsk, located in the Tula region, bordering the Moscow region that has many names translated from Sanskrit. Literally, Novomoskovsk means “New Moscow”. In Hindi, ‘Navi’ means ‘New’. New York and Russia have old ties, going beyond the general history. So does the name Tula or Thule, mentioned in ancient Greek and Roman literature and cartography. Tula / Thule is another name of Hyperborea (“beyond the North Wind”), more precise Arctic Hyperborea proposed in some exoteric writings to be the ancient origin of the Aryan race. It has nothing to do with Nazis and their Thule Society, who exploited this knowledge to justify their sinister deeds and crimes.
In a number of ancient sources, including the late Antiquarian and Roman texts, the Don River is called Sind. Exactly the same name was given on the ancient times to the river Sind in Hindustan. The Sindi were an ancient people in the Taman Peninsula, on Kerch Strait connecting the Azov Sea (the Don delta) and the Black Sea. Modern Sindh is a major province of Pakistan. Historically, Sindh is the home to the Sindhi people. Sindh’s capital Karachi has many “linguistic brothers” in Russia.
Based on the data of mythology and toponymy, established is the fact of transfer by the Aryans of geographical names from their Northern homeland (Northern Kuru, modern-day Russia) to their historical homeland Hindostan, a geographic term for the Indo-Gangetic Plain in northern India, broadly the Indian subcontinent, which later became an endonym. It is well known that the word Sindh is the basis for “Hind” of Hindustan. It is believed to come from the Persian (the Farsi). In the name Sind, S is pronounced as H in Farsi, so it became Hind. Hence, Sind → Hind → Hindustan. Overall, the Southern Siberia is considered to be the distant motherland of the Aryans, who created Vedic civilization in Hindustan and Avestan civilization in Iran.
Toponymy is at the junction of linguistics, history, and geography. Often, toponymy can say more than archaeological research. A lot of toponymy / hydronyms in the basin (interfluve) of the rivers Volga and Oka are practically identical with the names of sacred rivers and reservoirs in the Mahabharata, the first major Sanskrit epics of ancient India. The second one is Ramayaṇa. Interestingly, Ra was the earlier Scythian name of the Volga. In the works of ancient authors of the first centuries of AD, such as Claudius Ptolemy and Ammianus Marcellinus, the Volga was called Ra.
Ranha is “mythical stream” of the Avesta, the primary collection of religious texts of Zoroastrianism, whose founder is believed to be born on the Sanskrit named river Kama (the largest tributary of the Volga), near Russian city of Perm. Hydronyms, especially the names of large rivers, are the most stable in time. In Sanskrit, Rasa is “dew, juice, mythical river”. Exactly the same meaning has the Russian word ‘rosa’, often associated with God’s dew. The ToRah (the Old Testament) states that in the morning, after dew, appeared the Manna of Heaven.
 изливаются серебряные струи, представляющие реки Дон и Шат. Аналогичный сюжет слияния двух рек с санскритскими названиями Сухона и Юг изображен на гербе Великого Устюга – города Водолея. В Индии праздник кувшинов называется Кумбх Мела и является самым большим религиозным фестивалем на планете. Цвета кувшинов и рек на гербе Новомосковска тоже символичны. По сути, это два Вселенских начала: золото (Солнце) и серебро (Луна), Мужское и Женское. В определенной мере — идея Интеграции полярностей.
изливаются серебряные струи, представляющие реки Дон и Шат. Аналогичный сюжет слияния двух рек с санскритскими названиями Сухона и Юг изображен на гербе Великого Устюга – города Водолея. В Индии праздник кувшинов называется Кумбх Мела и является самым большим религиозным фестивалем на планете. Цвета кувшинов и рек на гербе Новомосковска тоже символичны. По сути, это два Вселенских начала: золото (Солнце) и серебро (Луна), Мужское и Женское. В определенной мере — идея Интеграции полярностей.
 детей. Только за период с 1962 по 1980 годы её книги были опубликованы тиражом почти 22 млн. экземпляров. Она – признанный создатель серии произведений о Ленине и его семье. В своих книгах она раскрывала человеческие качества будущего вождя мирового пролетариата, когда он был ёще ребенком и особенно его любовь к маме. Мать оказывает ключевое влияние на формирование личности ребёнка, является нравственным примером для своих детей. Её отцом (и дедом Ленина) был Александр Дмитриевич Бланк (1799 — 1870) родовое имение которого находилось под Казанью в нынешнем Ленино-Кокушкино. Александр Бланк умер 17 июля. Это же день убийства Андрея Боголюбского и Николая II – первого и последнего русского самодержца.
детей. Только за период с 1962 по 1980 годы её книги были опубликованы тиражом почти 22 млн. экземпляров. Она – признанный создатель серии произведений о Ленине и его семье. В своих книгах она раскрывала человеческие качества будущего вождя мирового пролетариата, когда он был ёще ребенком и особенно его любовь к маме. Мать оказывает ключевое влияние на формирование личности ребёнка, является нравственным примером для своих детей. Её отцом (и дедом Ленина) был Александр Дмитриевич Бланк (1799 — 1870) родовое имение которого находилось под Казанью в нынешнем Ленино-Кокушкино. Александр Бланк умер 17 июля. Это же день убийства Андрея Боголюбского и Николая II – первого и последнего русского самодержца. Магнитогорским металлургическим комбинатом, расположенном в 90 км. к северу от Аркаима. Символично, что в названии Магнитной, давшей название комбинату, присутствует имя индийского бога огня Агни. Это главный из земных богов, посредник между ними и людьми. Вайшванара или «всенародный» — эпитет Агни. По числу упоминаний в «Ригведе», он уступает только главному божеству ведийского пантеона Индре.
Магнитогорским металлургическим комбинатом, расположенном в 90 км. к северу от Аркаима. Символично, что в названии Магнитной, давшей название комбинату, присутствует имя индийского бога огня Агни. Это главный из земных богов, посредник между ними и людьми. Вайшванара или «всенародный» — эпитет Агни. По числу упоминаний в «Ригведе», он уступает только главному божеству ведийского пантеона Индре. начала работы внешней разведки по атомной тематике, курировал создание советской атомной бомбы. Под его личную ответственность Сталин назначил руководителем советского атомного проекта Курчатова.
начала работы внешней разведки по атомной тематике, курировал создание советской атомной бомбы. Под его личную ответственность Сталин назначил руководителем советского атомного проекта Курчатова. транспортных коридоров.
транспортных коридоров. в 1962 году.
в 1962 году. Фамилия Сталин на санскрите означает «обладающий сосудом». Действительно, он был сосудом знаний. Писатель-историк Рой Медведев сообщает, что Сталин читал по несколько книг в день и около тысячи книг в год. Сам Сталин говорил, что его дневная норма — страниц 500. Его библиотека была уникальной, как и его учителя — Ивана Грозного.
Фамилия Сталин на санскрите означает «обладающий сосудом». Действительно, он был сосудом знаний. Писатель-историк Рой Медведев сообщает, что Сталин читал по несколько книг в день и около тысячи книг в год. Сам Сталин говорил, что его дневная норма — страниц 500. Его библиотека была уникальной, как и его учителя — Ивана Грозного.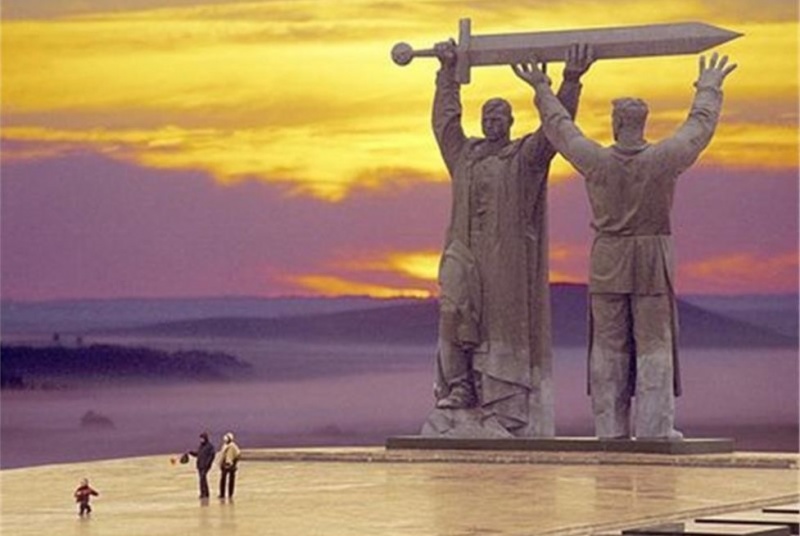
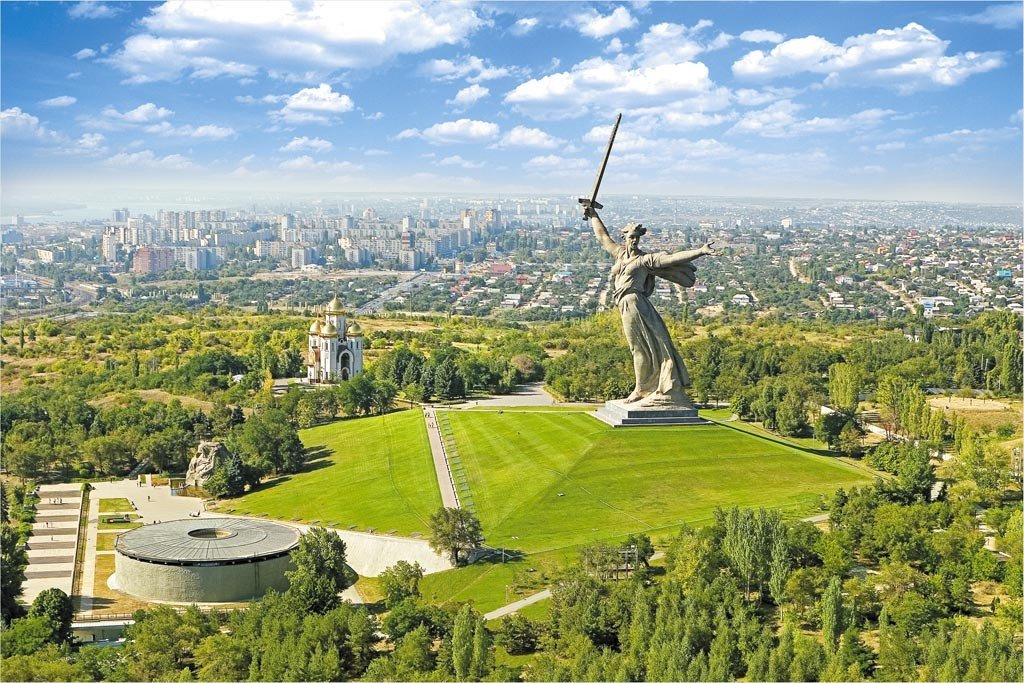


 В 15 км. к югу от современного Воронежа, на берегу Дона, расположены Костёнки – самая древняя система стоянок современного человека (лат. Homo sapiens). На сегодня обнаружено более 60 стоянок, возрастом от 15 до 45 тыс. лет. Найденные археологами артефакты свидетельствуют о высоком уровне культуры и искусства древних обитателей Костёнок. Это ставит под серьёзное сомнение теорию о том, что Человек разумный (лат. Homo sapiens) зародился в Африке и оттуда перекочевал на север Евразии. Исходя из возраста находок в Костёнках, делается предположение, что именно отсюда началось заселение современным человеком Евразийского континента.
В 15 км. к югу от современного Воронежа, на берегу Дона, расположены Костёнки – самая древняя система стоянок современного человека (лат. Homo sapiens). На сегодня обнаружено более 60 стоянок, возрастом от 15 до 45 тыс. лет. Найденные археологами артефакты свидетельствуют о высоком уровне культуры и искусства древних обитателей Костёнок. Это ставит под серьёзное сомнение теорию о том, что Человек разумный (лат. Homo sapiens) зародился в Африке и оттуда перекочевал на север Евразии. Исходя из возраста находок в Костёнках, делается предположение, что именно отсюда началось заселение современным человеком Евразийского континента.


 На берегу реки Хопёр – крупнейшем левом притоке Дона — стоит самый Урюпинск, являющийся самым западным городом Волгоградской области. В прессе и литературе его нередко называют «Столицей российской провинции». В этом городе происходят действия легендарного советского фильма «Судьба человека» по рассказу Михаила Шолохова, на основе реальных событий участника Великой Отечественной войны и друга Шолохова Николая Каргина. Он много сделал для станицы Вёшенская, где и жил в соседстве с великим писателем.
На берегу реки Хопёр – крупнейшем левом притоке Дона — стоит самый Урюпинск, являющийся самым западным городом Волгоградской области. В прессе и литературе его нередко называют «Столицей российской провинции». В этом городе происходят действия легендарного советского фильма «Судьба человека» по рассказу Михаила Шолохова, на основе реальных событий участника Великой Отечественной войны и друга Шолохова Николая Каргина. Он много сделал для станицы Вёшенская, где и жил в соседстве с великим писателем.

 Митра — головной убор и часть богослужебного облачения священнослужителя в православной церкви. Она напоминает о терновом венце, которым был коронован Христос. Митра также понимается как образ золотых венцов, которыми венчаются «праведники в Царстве Небесном на брачном пире сочетания Иисуса Христа с Церковью». Исторически митра на
Митра — головной убор и часть богослужебного облачения священнослужителя в православной церкви. Она напоминает о терновом венце, которым был коронован Христос. Митра также понимается как образ золотых венцов, которыми венчаются «праведники в Царстве Небесном на брачном пире сочетания Иисуса Христа с Церковью». Исторически митра на  одна из древнейших религий. В её основе лежит свободный нравственный выбор человеком благих мыслей, благих слов и благих деяний. Зороастризм содержит как
одна из древнейших религий. В её основе лежит свободный нравственный выбор человеком благих мыслей, благих слов и благих деяний. Зороастризм содержит как  От санскритского слова «митра» произошло
От санскритского слова «митра» произошло  Первым храмом во имя святителя Митрофана была надвратная церковь в Хотьковском монастыре, которую в 18
Первым храмом во имя святителя Митрофана была надвратная церковь в Хотьковском монастыре, которую в 18
 Гербы Великого Устюга и Воронежа связывают сюжет Водолея. На гербе Великого Устюга изображен Водолей с двумя кувшинами, символизирующими реки
Гербы Великого Устюга и Воронежа связывают сюжет Водолея. На гербе Великого Устюга изображен Водолей с двумя кувшинами, символизирующими реки  память о
память о 
 веке в Великом Новгороде, но история не знает, почему этот образ Благовещения был назван Устюжским и кем. В Устюге это была одна из самых почитаемых икон. У неё и
веке в Великом Новгороде, но история не знает, почему этот образ Благовещения был назван Устюжским и кем. В Устюге это была одна из самых почитаемых икон. У неё и 




 Видимо не случайно при обратном прочтении английского слова «Dog» (собака) получается другое английское слово – «God», т.е. Бог.
Видимо не случайно при обратном прочтении английского слова «Dog» (собака) получается другое английское слово – «God», т.е. Бог. Христофор занимает одно из центральных мест в западноевропейской герметической мысли, которая вышла из Египта и Ближнего Востока. Конечной целью инициации является становление адептом действительным Богочеловеком, Христом, пробуждение к жизни Сына Божьего, которого человек носит в глубине своего сердца, часто даже не подозревая об этом.
Христофор занимает одно из центральных мест в западноевропейской герметической мысли, которая вышла из Египта и Ближнего Востока. Конечной целью инициации является становление адептом действительным Богочеловеком, Христом, пробуждение к жизни Сына Божьего, которого человек носит в глубине своего сердца, часто даже не подозревая об этом.


 Иван Грозный разбил Ливонский орден в XVI веке. Последний глава Ливонского ордена принял светский титул герцога Курляндии и стал её главой. Курляндия (Курземе) находится в западной части Латвии, на берегу Балтийского моря. В названии этой исторической области примечателен корень «
Иван Грозный разбил Ливонский орден в XVI веке. Последний глава Ливонского ордена принял светский титул герцога Курляндии и стал её главой. Курляндия (Курземе) находится в западной части Латвии, на берегу Балтийского моря. В названии этой исторической области примечателен корень «




 Федоровича Романова, сына Патриарха Филарета (в миру — Фёдора Никитича
Федоровича Романова, сына Патриарха Филарета (в миру — Фёдора Никитича  Современная икона святого Христофора есть в верхнем ряду иконостаса храма Александра Невского на Патриаршем подворье при бывшей Покровской богадельне, на территории бывшего царского села Покровское-Рубцово. Христофор изображен с человеческой головой, но пёсья голова изображена отдельно внизу, не вызывая нареканий. Изначально, этот домовый храм Александра Невского при Покровской богадельне был освящен в 1858 году, но самый первый московский храм во имя этого святого, по преданию, был освящён в царствование первого Романова, Михаила Федоровича.
Современная икона святого Христофора есть в верхнем ряду иконостаса храма Александра Невского на Патриаршем подворье при бывшей Покровской богадельне, на территории бывшего царского села Покровское-Рубцово. Христофор изображен с человеческой головой, но пёсья голова изображена отдельно внизу, не вызывая нареканий. Изначально, этот домовый храм Александра Невского при Покровской богадельне был освящен в 1858 году, но самый первый московский храм во имя этого святого, по преданию, был освящён в царствование первого Романова, Михаила Федоровича. освящён деревянный храм во имя Николая Чудотворца. Позже был построен каменный храм в честь
освящён деревянный храм во имя Николая Чудотворца. Позже был построен каменный храм в честь  не особо её жаловал.
не особо её жаловал. расположен на острове Каменном. В народе его часто называют Спас-Камень. Интересная расшифровка слова «Камень» дана в статье «Новый код эволюции» («Мировой Ченнелинг» №1 за 2016):
расположен на острове Каменном. В народе его часто называют Спас-Камень. Интересная расшифровка слова «Камень» дана в статье «Новый код эволюции» («Мировой Ченнелинг» №1 за 2016): Кирилла с Папой Римским Франциском. Патриарх подарил Папе именно Казанскую икону Богоматери. Это единственная икона, побывавшая в
Кирилла с Папой Римским Франциском. Патриарх подарил Папе именно Казанскую икону Богоматери. Это единственная икона, побывавшая в  Желтоводский Макариев монастырь расположен на левом берегу
Желтоводский Макариев монастырь расположен на левом берегу  Казанского ханства. Сразу три древних монастыря Поволжья носят имя святого Макария. Один из них – Макарьевская пустынь рядом со Свияжском, где находится известная фреска святого Христофора (Анубиса), сделанная по приказу Ивана Грозного (см. раздел I).
Казанского ханства. Сразу три древних монастыря Поволжья носят имя святого Макария. Один из них – Макарьевская пустынь рядом со Свияжском, где находится известная фреска святого Христофора (Анубиса), сделанная по приказу Ивана Грозного (см. раздел I). Джугашвили, умерший в
Джугашвили, умерший в 
 Премьера «Лебединого озера» (самого популярного балета
Премьера «Лебединого озера» (самого популярного балета 
 воинственные германские валькирии – дочери
воинственные германские валькирии – дочери  рыцарь Лоэнгрин — герой немецких произведений о короле
рыцарь Лоэнгрин — герой немецких произведений о короле  писатель Александр Грин (1880 — 1932) — автор знаменитой феерии «Алые паруса» о непоколебимой вере и всепобеждающей, возвышенной мечте, о том, что каждый может сделать для близкого чудо. Прототип героини «Алых парусов» стала его вторая жена
писатель Александр Грин (1880 — 1932) — автор знаменитой феерии «Алые паруса» о непоколебимой вере и всепобеждающей, возвышенной мечте, о том, что каждый может сделать для близкого чудо. Прототип героини «Алых парусов» стала его вторая жена  здешнего Камско-Воткинского горного завода, где занимался обустройством и реорганизацией железоделательного производства. С XVIII по XX века завод являлся одним из самых передовых, был крупнейшим российским производителем якорей,
здешнего Камско-Воткинского горного завода, где занимался обустройством и реорганизацией железоделательного производства. С XVIII по XX века завод являлся одним из самых передовых, был крупнейшим российским производителем якорей, различного оружия. В середине ХХ века завод начал массовое производство баллистических ракет, которые являются ядром российских ядерных сил и основой ядерной триады России.
различного оружия. В середине ХХ века завод начал массовое производство баллистических ракет, которые являются ядром российских ядерных сил и основой ядерной триады России. Санкт-Петербурге, стоящим на
Санкт-Петербурге, стоящим на 




 расположен старейший мемориальный музыкальный музей в России, созданный почти сразу после смерти великого композитора.
расположен старейший мемориальный музыкальный музей в России, созданный почти сразу после смерти великого композитора. них были воспитаны несколько поколений советских детей. Журнал «Мировой Ченнелинг» даёт интересную информацию об этом человеке и откуда он черпал образы для своих произведений, см.
них были воспитаны несколько поколений советских детей. Журнал «Мировой Ченнелинг» даёт интересную информацию об этом человеке и откуда он черпал образы для своих произведений, см.  Мокша — это название реки в Центральной России. Её источник находится в 530 км. к юго-востоку от Москвы, недалеко от поселка городского типа Мокшан в Пензенской области. Мокшан стоит по обоим
Мокша — это название реки в Центральной России. Её источник находится в 530 км. к юго-востоку от Москвы, недалеко от поселка городского типа Мокшан в Пензенской области. Мокшан стоит по обоим  берегам Мокши. Длина этой реки ~
берегам Мокши. Длина этой реки ~  Мокша течёт на Запад и впадает в
Мокша течёт на Запад и впадает в  слову Сансара / Самсара («блуждание, странствование»), означающему круговорот рождения и смерти (реинкарнации) в мирах, ограниченных кармой. Это одно из основных понятий в индийской философии. Сансара рассматривается как результат невежества в понимании своего истинного «Я», невежества, под влиянием которого человек принимает временный и иллюзорный мир за реальность вообще. Душа, тонущая в «океане сансары», стремится к освобождению (мокше). Освобождение от Сансары называется Мокшей, как река, где расположен Санаксарский монастырь (или наоборот).
слову Сансара / Самсара («блуждание, странствование»), означающему круговорот рождения и смерти (реинкарнации) в мирах, ограниченных кармой. Это одно из основных понятий в индийской философии. Сансара рассматривается как результат невежества в понимании своего истинного «Я», невежества, под влиянием которого человек принимает временный и иллюзорный мир за реальность вообще. Душа, тонущая в «океане сансары», стремится к освобождению (мокше). Освобождение от Сансары называется Мокшей, как река, где расположен Санаксарский монастырь (или наоборот). В России говорили, что «где Ушаков, там и победа», но сначала он победил себя, свои человеческие слабости, стал добрым и честным, храбрым и скромным, милосердным к своим врагам и т.д. Он полностью отказался от своих личных интересов, посвятив свою жизнь России. Адмирал Ушаков был канонизирован Русской Православной Церковью в 2001 году. Его память — 5 августа (прославление). Это тот день, когда были закончены два знаковых сражения в истории человечества – Курская битва и битва на поле
В России говорили, что «где Ушаков, там и победа», но сначала он победил себя, свои человеческие слабости, стал добрым и честным, храбрым и скромным, милосердным к своим врагам и т.д. Он полностью отказался от своих личных интересов, посвятив свою жизнь России. Адмирал Ушаков был канонизирован Русской Православной Церковью в 2001 году. Его память — 5 августа (прославление). Это тот день, когда были закончены два знаковых сражения в истории человечества – Курская битва и битва на поле 
 Урий – это древнеегипетский символ власти фараона, силы жизни и смерти, способности уничтожать врагов бога Ра. Ра — древнее название вышеупомянутой реки Волга. Урий был священным змеем (коброй), которого фараон носил на лобовой части своей короны или диадемы. В индийской мифологии Вишну опирается на тысячеглавого змея
Урий – это древнеегипетский символ власти фараона, силы жизни и смерти, способности уничтожать врагов бога Ра. Ра — древнее название вышеупомянутой реки Волга. Урий был священным змеем (коброй), которого фараон носил на лобовой части своей короны или диадемы. В индийской мифологии Вишну опирается на тысячеглавого змея  Сканов монастырь расположен в нескольких километрах от вышеупомянутой реки Мокша. Он был основан в XVII веке. После 1917 года монастырь был закрыт. В 1985 году здания Скановского монастыря были возвращены Русской Православной Церкви. Первая обновленная служба состоялась в 1990 году 12 апреля, в День космонавтики. Именно в этот день в 1961 году,
Сканов монастырь расположен в нескольких километрах от вышеупомянутой реки Мокша. Он был основан в XVII веке. После 1917 года монастырь был закрыт. В 1985 году здания Скановского монастыря были возвращены Русской Православной Церкви. Первая обновленная служба состоялась в 1990 году 12 апреля, в День космонавтики. Именно в этот день в 1961 году,  “All is number” stated Pythagoras, the most famous Greek mathematician and philosopher, lived in the 6th century BCE. The intimate nature of cosmic harmony is mathematics. Everything in the Universe can be expressed in terms of whole (“natural”) numbers. Pythagorean numbers were hieroglyphic symbols he used to explain ideas relating to the nature of things. In Pythagorean system every number on Earth (that is the world of consequences) corresponds to its invisible prototype in the world of matters.
“All is number” stated Pythagoras, the most famous Greek mathematician and philosopher, lived in the 6th century BCE. The intimate nature of cosmic harmony is mathematics. Everything in the Universe can be expressed in terms of whole (“natural”) numbers. Pythagorean numbers were hieroglyphic symbols he used to explain ideas relating to the nature of things. In Pythagorean system every number on Earth (that is the world of consequences) corresponds to its invisible prototype in the world of matters. turning-point in the human history. In metaphysical sources, it was supposed to awaken human ancient memory. The humanity has fallen asleep in amnesia of materialism (within the
turning-point in the human history. In metaphysical sources, it was supposed to awaken human ancient memory. The humanity has fallen asleep in amnesia of materialism (within the  is the fifth chakra, called Vishudha. It is associated with
is the fifth chakra, called Vishudha. It is associated with  to a new level of consciousness (from the material to the spiritual). The first Russian Tsar Ivan Grozny was baptized on the day of the Beheading of John the Baptist in 1530 in the
to a new level of consciousness (from the material to the spiritual). The first Russian Tsar Ivan Grozny was baptized on the day of the Beheading of John the Baptist in 1530 in the  Nuclear-powered submarine “Kursk” was the pride of the Russian navy and represented the highest achievement of Soviet nuclear submarine technology. Submarines of this class were the second-largest attack submarines ever built, after another Soviet submarine class “Akula” (Project 941). The “Kursk” was compared to a leviathan with an almost mythical reputation as a war machine.
Nuclear-powered submarine “Kursk” was the pride of the Russian navy and represented the highest achievement of Soviet nuclear submarine technology. Submarines of this class were the second-largest attack submarines ever built, after another Soviet submarine class “Akula” (Project 941). The “Kursk” was compared to a leviathan with an almost mythical reputation as a war machine.
 The greatest ancient mystery is The Great Pyramid. Among other riddles it is linked to the mystery of 11. In the book of G. Henkoke and R. Bauval “The mystery of Sphinx” it is said that one of the chief numerical coefficients in the construction of The Great Pyramid and the entire necropolis in The Giza is 11. This number can be divided without a remainder only on itself and one. In the architecture of The Great Pyramid appear numbers divisible 11. For example the side of its foundation is 440 Egyptian cubits i.e. 11 x 40 cubits. The relation of the height to the foundation is 7:11. The incline of the side verges is 14:11 and the incline of the Southern shaft of The King’s Chamber is 11:11.
The greatest ancient mystery is The Great Pyramid. Among other riddles it is linked to the mystery of 11. In the book of G. Henkoke and R. Bauval “The mystery of Sphinx” it is said that one of the chief numerical coefficients in the construction of The Great Pyramid and the entire necropolis in The Giza is 11. This number can be divided without a remainder only on itself and one. In the architecture of The Great Pyramid appear numbers divisible 11. For example the side of its foundation is 440 Egyptian cubits i.e. 11 x 40 cubits. The relation of the height to the foundation is 7:11. The incline of the side verges is 14:11 and the incline of the Southern shaft of The King’s Chamber is 11:11. According to English mystic writer Alice Bailey (“From Bethlehem to Calvary”), Jesus Christ (the Saviour) demonstrated to mankind five degrees of ascent or five initiations, described in Gospel: Birth, Baptism, Transfiguration, Crucifixion, Resurrection and Ascension. Everyone on the planet Earth is now on one of these steps.
According to English mystic writer Alice Bailey (“From Bethlehem to Calvary”), Jesus Christ (the Saviour) demonstrated to mankind five degrees of ascent or five initiations, described in Gospel: Birth, Baptism, Transfiguration, Crucifixion, Resurrection and Ascension. Everyone on the planet Earth is now on one of these steps. The Aquarius is the heavenly patron of Russia. It has been entrusted with a special task and responsibility within the
The Aquarius is the heavenly patron of Russia. It has been entrusted with a special task and responsibility within the  Veliky Ustyug in January 2008 for Christmas service in the church of the founder of the
Veliky Ustyug in January 2008 for Christmas service in the church of the founder of the  The official date of establishing Veliky Ustyug is the year 1147 (4 + 7 = 11). Russian capital
The official date of establishing Veliky Ustyug is the year 1147 (4 + 7 = 11). Russian capital  is the only city in Russia (and probably in the world) that has Aquarius on its coat of arms. It was approved in the 18th century by the Russian Empress Catherine the Great.
is the only city in Russia (and probably in the world) that has Aquarius on its coat of arms. It was approved in the 18th century by the Russian Empress Catherine the Great. Karnataka, former the Kingdom of Mysore, is a state in the south western India. The coat of arms of Karnataka is based on that of the Kingdom of Mysore. That state was enlarged in 1956 and renamed Karnataka in
Karnataka, former the Kingdom of Mysore, is a state in the south western India. The coat of arms of Karnataka is based on that of the Kingdom of Mysore. That state was enlarged in 1956 and renamed Karnataka in  The official emblem of the Karnataka state government is a two-headed bird Gandaberunda, depicted on the state coat of arms. It is topped by the Lion Capital of
The official emblem of the Karnataka state government is a two-headed bird Gandaberunda, depicted on the state coat of arms. It is topped by the Lion Capital of  In Karnataka there is a homestead and graves of Svyatoslav Roerich and his wife Devika Rani (see below). Parents of Svyatoslav
In Karnataka there is a homestead and graves of Svyatoslav Roerich and his wife Devika Rani (see below). Parents of Svyatoslav  Roerich met in Bologoye,
Roerich met in Bologoye,  In the clutches of the Hittite double-headed eagle there were two victims. In the Russian coat of
In the clutches of the Hittite double-headed eagle there were two victims. In the Russian coat of arms, royal regalia are used instead of them, a scepter and a power. Gandaberunda is usually depicted as carrying in its paws elephants and lions. A similar motive is present at the church of St. Dmitry Solunsky (St. Demetrios of Thessaloniki) in the Russian town of
arms, royal regalia are used instead of them, a scepter and a power. Gandaberunda is usually depicted as carrying in its paws elephants and lions. A similar motive is present at the church of St. Dmitry Solunsky (St. Demetrios of Thessaloniki) in the Russian town of  Tataguni Estate of Svyatoslav Roerich and his wife Devika Rani, the star of Indian cinema and the great niece of the great poet Rabindranath Tagore, the first non-European who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature.
Tataguni Estate of Svyatoslav Roerich and his wife Devika Rani, the star of Indian cinema and the great niece of the great poet Rabindranath Tagore, the first non-European who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature.

 Chakra is the highest Indian order of peacetime. In the Yaroslavl region, 25 km from
Chakra is the highest Indian order of peacetime. In the Yaroslavl region, 25 km from  The above-mentioned village of Almatti has given its name to the famous Almatti Dam on the Krishna River, being one of the longest rivers in India. The Krishna River carries its waters from the Western Ghats to the Bay of Bengal through the Deccan Plateau. In Sanskrit, “alimat” means “swarm with bees”.
The above-mentioned village of Almatti has given its name to the famous Almatti Dam on the Krishna River, being one of the longest rivers in India. The Krishna River carries its waters from the Western Ghats to the Bay of Bengal through the Deccan Plateau. In Sanskrit, “alimat” means “swarm with bees”. The above mentioned Indian Almatti has certain linguistic and cultural ties with Kazakhstan Almaty, located 2,990 km north from Almatti. Moreover, Almaty and Almatti virtually lie on the same meridian.
The above mentioned Indian Almatti has certain linguistic and cultural ties with Kazakhstan Almaty, located 2,990 km north from Almatti. Moreover, Almaty and Almatti virtually lie on the same meridian. Kyrgyzstan is one of the deepest lakes of the planet, and is located 70 km to the south from the Lake Issyk (Kazakhstan). In 1969, near this lake was discovered the Issyk gold man (
Kyrgyzstan is one of the deepest lakes of the planet, and is located 70 km to the south from the Lake Issyk (Kazakhstan). In 1969, near this lake was discovered the Issyk gold man ( historical and sacral values described in the below sections of this work. They are largely based on the Volga, being a spiritual gift from Creator.
historical and sacral values described in the below sections of this work. They are largely based on the Volga, being a spiritual gift from Creator.

 are: the An-124 long-range heavy transport aircraft, the 200-seat Tu-204 medium-range airliner, modernized Il-76, etc.
are: the An-124 long-range heavy transport aircraft, the 200-seat Tu-204 medium-range airliner, modernized Il-76, etc. class of ramp vessels in the world. It can be operated in any climatic conditions with almost no restrictions. It could be used in various fields: as a military transport aircraft, aerial refueling tanker or command center, for extinguishing fires, etc. IL-76MD-90A is more unpretentious in comparison with the western one. It does not need a special infrastructure, and it does not need constant significant maintenance. They intend to create also a civilian version of the aircraft.
class of ramp vessels in the world. It can be operated in any climatic conditions with almost no restrictions. It could be used in various fields: as a military transport aircraft, aerial refueling tanker or command center, for extinguishing fires, etc. IL-76MD-90A is more unpretentious in comparison with the western one. It does not need a special infrastructure, and it does not need constant significant maintenance. They intend to create also a civilian version of the aircraft. In Old Maina there is a monument dedicated to the children who worked as hard as the adults during the World War II to crush the Nazis. On that monument it is written that Russia can not be defeated.
In Old Maina there is a monument dedicated to the children who worked as hard as the adults during the World War II to crush the Nazis. On that monument it is written that Russia can not be defeated. the mouth of local river Maina. According to Ulyanovsk archaeologists, in the territory of the present Old Maina people have been living continuously since the 3rd – 4th century. The tribes of Imenkovo archaeological culture came first here. Many official researchers regard Imenkovo culture as the Slavs. More profound results on the ancestors of the Slavs provide
the mouth of local river Maina. According to Ulyanovsk archaeologists, in the territory of the present Old Maina people have been living continuously since the 3rd – 4th century. The tribes of Imenkovo archaeological culture came first here. Many official researchers regard Imenkovo culture as the Slavs. More profound results on the ancestors of the Slavs provide 
 Germanization or extermination started approximately in the 12th century, when the Danish feudal lords destroyed the ancient Slavic sanctuary of Arkona, located on the island of Ruyan (German Rügen) in the Baltic Sea.
Germanization or extermination started approximately in the 12th century, when the Danish feudal lords destroyed the ancient Slavic sanctuary of Arkona, located on the island of Ruyan (German Rügen) in the Baltic Sea.


 stone church in Kiev, built in the end of 10th century by the order of Grand Prince Vladimir the Great, who Christianized the Kievan Rus. Kiev was the main center of Christianization of other parts of Rus (Russia). Hence, it was called “mother of Russian cities” in Greek manner. The Greeks (from Byzantium) took the most active role in spreading Christianity in Russia. The expression “mother of Russian cities”, as well as the Greek “metropolis” (from “meter” – “mother” and “polis” – “city”), means the founding city. In Russian language, Kiev is a male name. Kiev reached its Golden Age as the center Kievan Rus in the 10th — 12th centuries.
stone church in Kiev, built in the end of 10th century by the order of Grand Prince Vladimir the Great, who Christianized the Kievan Rus. Kiev was the main center of Christianization of other parts of Rus (Russia). Hence, it was called “mother of Russian cities” in Greek manner. The Greeks (from Byzantium) took the most active role in spreading Christianity in Russia. The expression “mother of Russian cities”, as well as the Greek “metropolis” (from “meter” – “mother” and “polis” – “city”), means the founding city. In Russian language, Kiev is a male name. Kiev reached its Golden Age as the center Kievan Rus in the 10th — 12th centuries. deeply involved in The Knight Templar in France and Palestine. The oldest settlement on the territory of modern-day Yaroslavl belongs to the 5th – 3rd millennium BCE. Apparently,
deeply involved in The Knight Templar in France and Palestine. The oldest settlement on the territory of modern-day Yaroslavl belongs to the 5th – 3rd millennium BCE. Apparently,  Sun, and not the Sun of the Solar System itself. Yaroslavl is the point of the Earth, which has always been directly connected with the energy flows of the Central Spiritual Sun. The bear is the ancient symbol of Yaroslavl, like Russia’s. According to a legend, when Yaroslav the Wise came here to baptize the local residents, he had to
Sun, and not the Sun of the Solar System itself. Yaroslavl is the point of the Earth, which has always been directly connected with the energy flows of the Central Spiritual Sun. The bear is the ancient symbol of Yaroslavl, like Russia’s. According to a legend, when Yaroslav the Wise came here to baptize the local residents, he had to  deal with their sacred and worshiped bear. It happened at the confluence of the Volga and the Kotorosl River.
deal with their sacred and worshiped bear. It happened at the confluence of the Volga and the Kotorosl River. administrative center is the town of
administrative center is the town of  Bolgal has special religious significance for the Muslims of Russia and the Volga river regions in particular. Islam was adopted here in 922 and it became official religion of the Volga Bulgaria. Special embassy arrived from Baghdad then capital of the Caliphate ruled by the Abbasid dynasty. The spread of Islam in the Middle Volga region was peaceful. The Volga Bulgarians knew One God from their pre-Islamic religion called Tengrism. The adoption of Islam by the Volga Bulgaria led to a strong impetus to the development of education, literature, and science. The Bolgars achieved considerable success in mathematics and astronomy, chemistry and medicine, geography and history. From the Soviet times, pilgrimage to Bolgar is called the Little Hajj.
Bolgal has special religious significance for the Muslims of Russia and the Volga river regions in particular. Islam was adopted here in 922 and it became official religion of the Volga Bulgaria. Special embassy arrived from Baghdad then capital of the Caliphate ruled by the Abbasid dynasty. The spread of Islam in the Middle Volga region was peaceful. The Volga Bulgarians knew One God from their pre-Islamic religion called Tengrism. The adoption of Islam by the Volga Bulgaria led to a strong impetus to the development of education, literature, and science. The Bolgars achieved considerable success in mathematics and astronomy, chemistry and medicine, geography and history. From the Soviet times, pilgrimage to Bolgar is called the Little Hajj. is more than 22% of the world’s population. The largest Koran is kept in Bolgar. The Volga Bulgaria was the only Islamic country of Eastern Europe. The Bulgarian Historical and Architectural Museum-Reserve (established in 1969) is the most northern monument in the world of medieval Muslim architecture. Being secular, the leadership of Tatarstan places a key importance on the development of historical and religious heritage. Bolgar is identified with Islam, whereas
is more than 22% of the world’s population. The largest Koran is kept in Bolgar. The Volga Bulgaria was the only Islamic country of Eastern Europe. The Bulgarian Historical and Architectural Museum-Reserve (established in 1969) is the most northern monument in the world of medieval Muslim architecture. Being secular, the leadership of Tatarstan places a key importance on the development of historical and religious heritage. Bolgar is identified with Islam, whereas  southeast of Old Maina, and 90 km southeast of Ulyanovsk. Only 9 km is to New Maina from the city of Dimitrovgrad.
southeast of Old Maina, and 90 km southeast of Ulyanovsk. Only 9 km is to New Maina from the city of Dimitrovgrad. New Maina and Dimitrovgrad are divided by the river called the Big Cheremshan (Russian: the Bolshoy Cheremshan River), a tributary of the Volga River.
New Maina and Dimitrovgrad are divided by the river called the Big Cheremshan (Russian: the Bolshoy Cheremshan River), a tributary of the Volga River. Obnisk (the Kaluga region), the place of the world’s first nuclear power plant to generate electricity for a power grid.
Obnisk (the Kaluga region), the place of the world’s first nuclear power plant to generate electricity for a power grid.
 the 5th millennium BCE. The Samara region is considered as the original homeland of the Proto-Indo-European language.
the 5th millennium BCE. The Samara region is considered as the original homeland of the Proto-Indo-European language. secretive bunker of its ruler Josef Stalin is now open to the public. After the war, Samara became the Cosmic capital of the Soviet Union. In Samara was built the launch vehicle Vostok, which delivered in 1961 the first manned spaceship to orbit with Yury Gagarin on board. After returning to Earth / landing near the great Russian River Volga,
secretive bunker of its ruler Josef Stalin is now open to the public. After the war, Samara became the Cosmic capital of the Soviet Union. In Samara was built the launch vehicle Vostok, which delivered in 1961 the first manned spaceship to orbit with Yury Gagarin on board. After returning to Earth / landing near the great Russian River Volga,  Yury Gagarin, the first man to travel in Space, took a rest in Samara. Here he reported to the State Commission, headed by Sergei Korolev, on the successful completion of his historical mission.
Yury Gagarin, the first man to travel in Space, took a rest in Samara. Here he reported to the State Commission, headed by Sergei Korolev, on the successful completion of his historical mission. The above described settlements Old Maina and New Maina of the Ulyanovsk region are located on the left bank of the River Volga. On the opposite right bank of the Volga, there is also settlement Maina and river Maina. This urban type settlement Maina is 50 km west south of Ulyanovsk, whose historical center is also on the right bank of the Volga. Interestingly, in Southern Siberia also there is settlement called
The above described settlements Old Maina and New Maina of the Ulyanovsk region are located on the left bank of the River Volga. On the opposite right bank of the Volga, there is also settlement Maina and river Maina. This urban type settlement Maina is 50 km west south of Ulyanovsk, whose historical center is also on the right bank of the Volga. Interestingly, in Southern Siberia also there is settlement called 
 The Avestan language is classified as an Iranian language, a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages within the Indo-European family. The Avestan is assumed to have been quite close to Vedic Sanskrit. In Russia there are many names of rivers and settlements translated from Sanskrit. For instance, in the Ulyanovsk region is the source of river Sura. In Sanskrit,
The Avestan language is classified as an Iranian language, a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages within the Indo-European family. The Avestan is assumed to have been quite close to Vedic Sanskrit. In Russia there are many names of rivers and settlements translated from Sanskrit. For instance, in the Ulyanovsk region is the source of river Sura. In Sanskrit,  70 km northwest from Maina is the settlement
70 km northwest from Maina is the settlement  Sura Peaks (Russian: Surskiye Vershiny). This place is famous for its St. Nicholas Hill overlooking the River Sura. It is one of the most revered destinations in the Sura district and the whole Russia. It is believed by everyone claimed the 76-meter hill will be freed from all the sins. This St. Nicholas Hill is made of chalk. Its slopes are very steep, covered with grass and rare bushes.
Sura Peaks (Russian: Surskiye Vershiny). This place is famous for its St. Nicholas Hill overlooking the River Sura. It is one of the most revered destinations in the Sura district and the whole Russia. It is believed by everyone claimed the 76-meter hill will be freed from all the sins. This St. Nicholas Hill is made of chalk. Its slopes are very steep, covered with grass and rare bushes. Alatyr, like the settlement Sura Hills, was established by the order of the first Russian Tsar Ivan Grozny going to conquer
Alatyr, like the settlement Sura Hills, was established by the order of the first Russian Tsar Ivan Grozny going to conquer  in the Aquila constellation), Altar (the ‘Holy table’, structure for religious sacrifices located in places of worship), etc.
in the Aquila constellation), Altar (the ‘Holy table’, structure for religious sacrifices located in places of worship), etc.  The source of river Alatyr is 190 km west of its mouth. The Alatyr originates in the
The source of river Alatyr is 190 km west of its mouth. The Alatyr originates in the  Between St. Nicholas Hill / the settlement Sura Hills and city of Alatyr is located village Sara and two Sarka rivers: The Big Sarka and the Small Sarka. Sarka is a diminutive of Sara (river). In Sanskrit, Sara means “essence”, “stream”, “energy”, “main point”, etc. The Middle Eastern name Sarah means “Princess”.
Between St. Nicholas Hill / the settlement Sura Hills and city of Alatyr is located village Sara and two Sarka rivers: The Big Sarka and the Small Sarka. Sarka is a diminutive of Sara (river). In Sanskrit, Sara means “essence”, “stream”, “energy”, “main point”, etc. The Middle Eastern name Sarah means “Princess”.
 that connect five seas: the Baltic, White, Caspian, Azov and Black seas. Shipping Volga – Don Canal named after
that connect five seas: the Baltic, White, Caspian, Azov and Black seas. Shipping Volga – Don Canal named after  is from the Soviet defenders during the Battle of Stalingrad (August 1942 – February 1943) that was the largest and bloodiest battle in the history of warfare.
is from the Soviet defenders during the Battle of Stalingrad (August 1942 – February 1943) that was the largest and bloodiest battle in the history of warfare.
 Rostselmash (founded in 1929) is a Russian agricultural equipment company, based in Rostov-on-Don. It is one of the five largest world producers of agricultural machinery. Beside Russia, Rostselmash has production facilities in Canada, USA, Ukraine and Kazakhstan.
Rostselmash (founded in 1929) is a Russian agricultural equipment company, based in Rostov-on-Don. It is one of the five largest world producers of agricultural machinery. Beside Russia, Rostselmash has production facilities in Canada, USA, Ukraine and Kazakhstan. one of the largest manufacturers of locomotives in the world. The plant has produced more than 16,000 locomotives of more than 65 types. Its locomotives haul trains transporting 80% of all cargo on the electrified railways of Russia and CIS countries. Russia has the longest railway in the world. The longest railway in Russia and on the planet is the Transsiberian Railway (9,300 km long), also called The Great Siberian Way, connecting Moscow with the Far Eastern industrial cities of Russia. Russia has a total length of 121,000 km of the railway tracks, most being located in picturesque areas.
one of the largest manufacturers of locomotives in the world. The plant has produced more than 16,000 locomotives of more than 65 types. Its locomotives haul trains transporting 80% of all cargo on the electrified railways of Russia and CIS countries. Russia has the longest railway in the world. The longest railway in Russia and on the planet is the Transsiberian Railway (9,300 km long), also called The Great Siberian Way, connecting Moscow with the Far Eastern industrial cities of Russia. Russia has a total length of 121,000 km of the railway tracks, most being located in picturesque areas. Throughout its history, it has designed and produced more than 20 different models of aircraft for civilian and military purposes, as well as customized models. Pilots flying Beriev seaplanes have broken 228 world aviation records.
Throughout its history, it has designed and produced more than 20 different models of aircraft for civilian and military purposes, as well as customized models. Pilots flying Beriev seaplanes have broken 228 world aviation records. In antiquity, the Don was viewed as the border between Europe and Asia by some ancient Greek geographers. Indeed, the modern boundary of Europe and Asia is drawn by the Manych, a tributary of the Don. The border passes along the tops of the Ural Mountains and further along the Kumo-Manych depression, which is now the floodplain of the Kuma and Manych rivers, but in ancient times was a strait connecting the Black Sea with the Caspian.
In antiquity, the Don was viewed as the border between Europe and Asia by some ancient Greek geographers. Indeed, the modern boundary of Europe and Asia is drawn by the Manych, a tributary of the Don. The border passes along the tops of the Ural Mountains and further along the Kumo-Manych depression, which is now the floodplain of the Kuma and Manych rivers, but in ancient times was a strait connecting the Black Sea with the Caspian. During the times of the
During the times of the  hero Hercules, searched for Colchis in the delta of River Don (the Azov Sea). Aea, later Colchis, was located in the lands of the Azov (not the Black) Sea. The name of Colchis was fixed by famous Ancient Greek lyric poet
hero Hercules, searched for Colchis in the delta of River Don (the Azov Sea). Aea, later Colchis, was located in the lands of the Azov (not the Black) Sea. The name of Colchis was fixed by famous Ancient Greek lyric poet 
 Dmitri was a prominent Russian Church theologian, Bishop of
Dmitri was a prominent Russian Church theologian, Bishop of  the spot where Mana River enters
the spot where Mana River enters  + sky”. In the middle of the last century, they considered this territory as a place for
+ sky”. In the middle of the last century, they considered this territory as a place for  Krasnoyarsk. Divnogorsk’s main industrial facility is the Krasnoyarsk Dam on the
Krasnoyarsk. Divnogorsk’s main industrial facility is the Krasnoyarsk Dam on the Yenisei River. From commissioning of 10th turbine in 1971, the station was the world’s single biggest power producer until 1983. It is a landmark symbol of Krasnoyarsk, and is depicted on the 10-ruble bill. As a result of the damming, the Krasnoyarsk Reservoir (informally the Krasnoyarsk Sea) was created. It is 388 km in length.
Yenisei River. From commissioning of 10th turbine in 1971, the station was the world’s single biggest power producer until 1983. It is a landmark symbol of Krasnoyarsk, and is depicted on the 10-ruble bill. As a result of the damming, the Krasnoyarsk Reservoir (informally the Krasnoyarsk Sea) was created. It is 388 km in length. The shield is topped with the golden mural crown. The lion symbolizes strength and courage. The sickle
The shield is topped with the golden mural crown. The lion symbolizes strength and courage. The sickle  and shovel initially reflected the main occupation of the inhabitants — farming and mining of minerals, primarily gold. In the 1840s the Yenisei province became the main center of
and shovel initially reflected the main occupation of the inhabitants — farming and mining of minerals, primarily gold. In the 1840s the Yenisei province became the main center of  arose in the 12th century as a patrimonial sign of the Vladimir princes. The image of a lion is one of the most common plots in the decorative design of the world famous temples built on the Vladimir land in the 12th -14th centuries. As a rule, lion in heraldry symbolizes strength, courage, power.
arose in the 12th century as a patrimonial sign of the Vladimir princes. The image of a lion is one of the most common plots in the decorative design of the world famous temples built on the Vladimir land in the 12th -14th centuries. As a rule, lion in heraldry symbolizes strength, courage, power. The sickle (of the Krasnoyarsk lion) is a multilevel symbol. In Greek mythology, the leader of
The sickle (of the Krasnoyarsk lion) is a multilevel symbol. In Greek mythology, the leader of  Yenisei competed for some time in documents with the South Siberian name of this river – Kem. Eventually, the term Yenisei has replaced Kem.
Yenisei competed for some time in documents with the South Siberian name of this river – Kem. Eventually, the term Yenisei has replaced Kem.
 Russia, including the above mentioned place Sungir near Vladimir, the previous capital of Russia. As a recall from the time of Lemurian Egypt, could be the shape of Krasnoyarsk local history museum (founded in 1889) stylized as the ancient Egyptian temple.
Russia, including the above mentioned place Sungir near Vladimir, the previous capital of Russia. As a recall from the time of Lemurian Egypt, could be the shape of Krasnoyarsk local history museum (founded in 1889) stylized as the ancient Egyptian temple. Luxor, located on the bank of Nile. By the way, in Latin, Lux means Light. The construction of Egyptian bulging of Krasnoyarsk local history museum started in 1913 and was finished in 1929. It is one of the oldest museums in Siberia and the Far East, one of the largest museums in Russia.
Luxor, located on the bank of Nile. By the way, in Latin, Lux means Light. The construction of Egyptian bulging of Krasnoyarsk local history museum started in 1913 and was finished in 1929. It is one of the oldest museums in Siberia and the Far East, one of the largest museums in Russia.
_%D0%BC%D0%BE%D0%B5.jpg) city is notable for its nature landscapes. The Krasnoyarsk Pillars (bordering the River Mana, a favorite recreation place for Krasnoyarsk residents and many tourists from different countries; the most spectacular loops River Mana makes near its mouth in settlement ManSky) are stone remains and megalithic structures that are also believed to
city is notable for its nature landscapes. The Krasnoyarsk Pillars (bordering the River Mana, a favorite recreation place for Krasnoyarsk residents and many tourists from different countries; the most spectacular loops River Mana makes near its mouth in settlement ManSky) are stone remains and megalithic structures that are also believed to  be made / used by previous civilizations with the purpose of using this place for moving between the worlds. Even a simple stay next to such a portal stimulates the growth and development of a person’s consciousness. At one life cycle of incarnation it is possible to make a huge leap.
be made / used by previous civilizations with the purpose of using this place for moving between the worlds. Even a simple stay next to such a portal stimulates the growth and development of a person’s consciousness. At one life cycle of incarnation it is possible to make a huge leap. Also, it is the day of the
Also, it is the day of the 
 in 1973. Originally, the Twin Towers were the tallest buildings in the world. Metaphysically, they represented the might of material world dominated on the planet within the
in 1973. Originally, the Twin Towers were the tallest buildings in the world. Metaphysically, they represented the might of material world dominated on the planet within the  Urban-type settlement of Maina is located on the bank of Yenisei River. Maina
Urban-type settlement of Maina is located on the bank of Yenisei River. Maina  hydroelectric power station is a counter-regulator of the Sayano-Shushenskaya hydroelectric power station, smoothing the fluctuations in the water level in the Yenisei that arise when the operating modes of this powerful Sayano-Shushenskaya HPP are changed (see below).
hydroelectric power station is a counter-regulator of the Sayano-Shushenskaya hydroelectric power station, smoothing the fluctuations in the water level in the Yenisei that arise when the operating modes of this powerful Sayano-Shushenskaya HPP are changed (see below). any analogs in Russia. During the year and during the day, the electricity needs are different. Therefore, Sayano-Shushenskaya hydroelectric station (peak HPP) must respond quickly to these fluctuations. Constant fluctuations in the water
any analogs in Russia. During the year and during the day, the electricity needs are different. Therefore, Sayano-Shushenskaya hydroelectric station (peak HPP) must respond quickly to these fluctuations. Constant fluctuations in the water Sayano-Shushenskaya hydroelectric power station is the largest power plant in Russia and the 9th largest hydroelectric plant in the world, by average power generation. The dam supports the Sayano–Shushenskoe reservoir with surface area of 621 km2.
Sayano-Shushenskaya hydroelectric power station is the largest power plant in Russia and the 9th largest hydroelectric plant in the world, by average power generation. The dam supports the Sayano–Shushenskoe reservoir with surface area of 621 km2. in exile here for 3 years, from 1897 to 1900. He also got married here in 1898. Lenin was one of two persons in the 20th century who were given the title of
in exile here for 3 years, from 1897 to 1900. He also got married here in 1898. Lenin was one of two persons in the 20th century who were given the title of  including the international flights. Many visitors from all over the Soviet Union and abroad would come here. In 1970, they opened a large museum-reserve dedicated to Lenin’s time in Shushenskoye (Siberia).
including the international flights. Many visitors from all over the Soviet Union and abroad would come here. In 1970, they opened a large museum-reserve dedicated to Lenin’s time in Shushenskoye (Siberia). The area around the above mentioned city of Abakan is full of ancient menhirs. Typically, these menhirs are vertically buried in the ground stone slabs. They could be up to three meters high and over one meter wide. These ancient stone sculptures have a sacred meaning. Similar structures are present in Western Europe and the Scottish island of Lewis of Harris.
The area around the above mentioned city of Abakan is full of ancient menhirs. Typically, these menhirs are vertically buried in the ground stone slabs. They could be up to three meters high and over one meter wide. These ancient stone sculptures have a sacred meaning. Similar structures are present in Western Europe and the Scottish island of Lewis of Harris. believed that these mysterious stone statues (menhirs) were erected by people who lived here about 4,000 years ago.
believed that these mysterious stone statues (menhirs) were erected by people who lived here about 4,000 years ago. The very name Abakan could be connected with Sanskrit. It is present in other Russian places where toponymy is translated from Sanskrit. For instance, village Abakanovo (meaning Little Abakan) is located in
The very name Abakan could be connected with Sanskrit. It is present in other Russian places where toponymy is translated from Sanskrit. For instance, village Abakanovo (meaning Little Abakan) is located in  plates. At the beginning of the excavation, the height of the mound reached 11.5 meters. The length of the stone fence was 71 m. The earth embankment / tetrahedral pyramid initially reached a height of approximately up to 25 m.
plates. At the beginning of the excavation, the height of the mound reached 11.5 meters. The length of the stone fence was 71 m. The earth embankment / tetrahedral pyramid initially reached a height of approximately up to 25 m. The height of vertically standing monoliths reaches 6 meters, plus at least 1 meter should be below the surface (otherwise they could not keep the upright position). The weight of stone monoliths fluctuates from 30 to 50 tons. It is suggested that the Scythians transported them from the quarries on the banks of the Yenisei River located 70 km from the mounds. None of the archaeologists involved can explain and show what transportation means were used. Even today,
The height of vertically standing monoliths reaches 6 meters, plus at least 1 meter should be below the surface (otherwise they could not keep the upright position). The weight of stone monoliths fluctuates from 30 to 50 tons. It is suggested that the Scythians transported them from the quarries on the banks of the Yenisei River located 70 km from the mounds. None of the archaeologists involved can explain and show what transportation means were used. Even today,  it would be a challenge for the modern powerful machinery like big tracks, excavators, and cranes.
it would be a challenge for the modern powerful machinery like big tracks, excavators, and cranes. Another evidence of the antiquity of the names around Abakan is the local Tasheba River (a tributary of the Yenisei). Teisheba is the Urartian god of thunder and war. He is a counterpart to the Assyrian god Adad, the Vedic God Indra, and the Hurrian god, Teshub. The Hurrians tribes represented a large ethnic component in the region of Lake Urmia, where the
Another evidence of the antiquity of the names around Abakan is the local Tasheba River (a tributary of the Yenisei). Teisheba is the Urartian god of thunder and war. He is a counterpart to the Assyrian god Adad, the Vedic God Indra, and the Hurrian god, Teshub. The Hurrians tribes represented a large ethnic component in the region of Lake Urmia, where the  The world’s oldest astronomical observatory is located in Khakassia. The observatory’s age comes to almost
The world’s oldest astronomical observatory is located in Khakassia. The observatory’s age comes to almost It is only 13 km from the Sunduki to the so called Siberian Dead Sea that is the Lake Tus. It is the most exotic lake in Eastern Siberia. The concentration of the salt (essence of life) is so high that it is impossible to dive or sink. The name of the lake is clearly
It is only 13 km from the Sunduki to the so called Siberian Dead Sea that is the Lake Tus. It is the most exotic lake in Eastern Siberia. The concentration of the salt (essence of life) is so high that it is impossible to dive or sink. The name of the lake is clearly  into the lake have been found on the South Western bank. At a depth of 5 to 10 meters, researchers have also found fragments of giant stone slabs. On the eastern side, 15 slabs with cut ends have been found. Obviously, no natural phenomenon can produce rectangles and lay them in a dense cover along the shore of the lake.
into the lake have been found on the South Western bank. At a depth of 5 to 10 meters, researchers have also found fragments of giant stone slabs. On the eastern side, 15 slabs with cut ends have been found. Obviously, no natural phenomenon can produce rectangles and lay them in a dense cover along the shore of the lake. The Krasnoyarsk Krai lies in the middle of Russia and Siberia. It is among the richest of Russia’s regions in natural resources. 80% of the country’s nickel, 75% of its cobalt, 70% of its copper, 16% of its coal, and 10% of its gold are extracted here. The Krasnoyarsk Krai also produces 20% of the country’s timber. More than 95% of Russian resources of platinum and platinoids are concentrated in the Krasnoyarsk Krai.
The Krasnoyarsk Krai lies in the middle of Russia and Siberia. It is among the richest of Russia’s regions in natural resources. 80% of the country’s nickel, 75% of its cobalt, 70% of its copper, 16% of its coal, and 10% of its gold are extracted here. The Krasnoyarsk Krai also produces 20% of the country’s timber. More than 95% of Russian resources of platinum and platinoids are concentrated in the Krasnoyarsk Krai.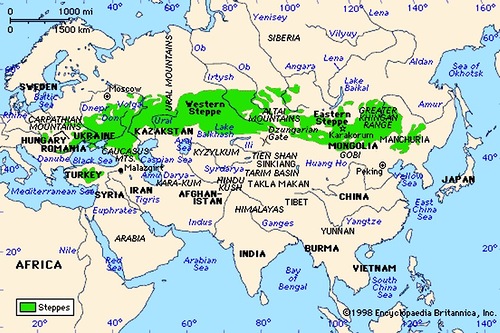 Siberia to the Black Sea region. The eastern border of the Aryan living space was
Siberia to the Black Sea region. The eastern border of the Aryan living space was  empire of the Persians, nor by Alexander the Great. The Scythians is the Greek word by which the Hellenes designated nomadic peoples living on the territory of the Black Sea region between the rivers Don and the Danube. The Russian River Don is famous for its brave
empire of the Persians, nor by Alexander the Great. The Scythians is the Greek word by which the Hellenes designated nomadic peoples living on the territory of the Black Sea region between the rivers Don and the Danube. The Russian River Don is famous for its brave  Finally, they decided to found the Academic Town on the western outskirts of the city of Krasnoyarsk, on the last vertex of the Sayan ridge, on the other bank of the Yenisei River. Steep bank, towering a hundred meters above the Yenisei, was chosen as the birthplace of the scientific nucleus.
Finally, they decided to found the Academic Town on the western outskirts of the city of Krasnoyarsk, on the last vertex of the Sayan ridge, on the other bank of the Yenisei River. Steep bank, towering a hundred meters above the Yenisei, was chosen as the birthplace of the scientific nucleus.

.jpg) 1,000 tons.
1,000 tons.



